Catechism Lessons
according to the Tradition of the Gospel and the Church
“Go, teach all nations...teaching them to observe all that I have commanded you.”
Holy Gospel of Jesus Christ,
St. Matthew 28:19-20
Lessons 1 to 4 ⇓
Take a quiz to test your knowledge:
Lessons 5 to 8 ⇓
Take a quiz to test your knowledge:
Lessons 9 to 12 ⇓
Lesson 1: The End of Man

1. — Who created Heaven and earth?

2. — What is man?

3. — How does our soul resemble God?

4. — Why did God create us?

5. — Should we take more care of our soul than of our body?

6. — What must we do to be saved?

7. — How shall we know the things that we must believe and practice?

8. — Where shall we find the principal truths that the Church teaches us?

9. — Recite the Apostles’ Creed.














Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio of the Lesson
Glossary
Creator: “Creator” is the name given to someone who creates – one who makes something out of nothing. This name can only be given to God.
To know God: To know that God IS; to know what His perfections are and what He wants us to do.
To love God: To unite with Him and seek to please Him.
To serve God: To obey His holy Will by doing what He commands.
Eternity: A duration that never ends. More exactly, an infinite relationship with God.
Lesson 2: God and His Perfections

10. — What is God?

11. — Did God have a beginning?

12. — Where is God?

13. — If God is everywhere, why do we not see Him?

14. — Does God see us?

15. — Does God know all things?

16. — Can God do all things?

17. — Is God just, holy and merciful?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio of the Lesson
Glossary
Spirit: A being that has no body and cannot be perceived by the senses. A spirit cannot be seen with the eyes, heard with the ears, smelled with the nose, tasted with the mouth, or touched with the hands.
Infinitely perfect: There is no flaw in God. Every imaginable quality is in Him, to absolute perfection.
God is everywhere: He is not confined to any place, no matter how great we can imagine it. He is in Heaven, on earth, in all places.
God is just: God gives to each one what is due to him, without causing harm to anyone and by a free effect of His Infinite Love.
God is merciful: God has a heart that has mercy on the unfortunate. He loves us and seeks to forgive us. He does everything to save us.
God is holy: God is infinitely perfect. He is the source of all love and Holiness. All that is evil is not, nor does it exist in God. God is infinite Goodness, Truth, Life and Beauty.
Lesson 3: The Unity and Trinity of God

18. —Is there only one God?

19. — Why can there be only one God?

20. — How many Persons are there in God?

21. — Is the Father God?

22. —Is the Son God?

23. — Is the Holy Spirit God?

24. — What do we mean by the Holy Trinity?

25. — Are the three divine Persons equal in all things?

26. — Why are the three divine Persons one and the same God?

27. —Can we understand how the three divine Persons are one and the same God?

28. — What is a mystery?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio of the Lesson
Glossary
Supreme Being: God is the Supreme Being because He is superior to all other beings, since He is their Creator.
Infinite: Without any limit. We say that the three divine Persons are distinct to show that They cannot be intermingled.
The Father is not the Son, the Son is not the Father, and the Holy Spirit is neither the Father nor the Son. The three divine Persons are equal in all things. This means that They have the same qualities, the same attributes. One is not more God than the Other. The three divine Persons have one and the same nature.
This means that They are one single Being and that They are not each an independent, separate Being. In other words, they are one and the same Essence.
Sovereign: One who is above all; supreme.
Christian: One who believes in Christ and keeps His Word.
Lesson 4: Creation

29. — Who created Heaven and earth?

30. — How did God create Heaven and earth?

31. — Which are the chief beings that God created?

32. — Why did God create all the things that we see?
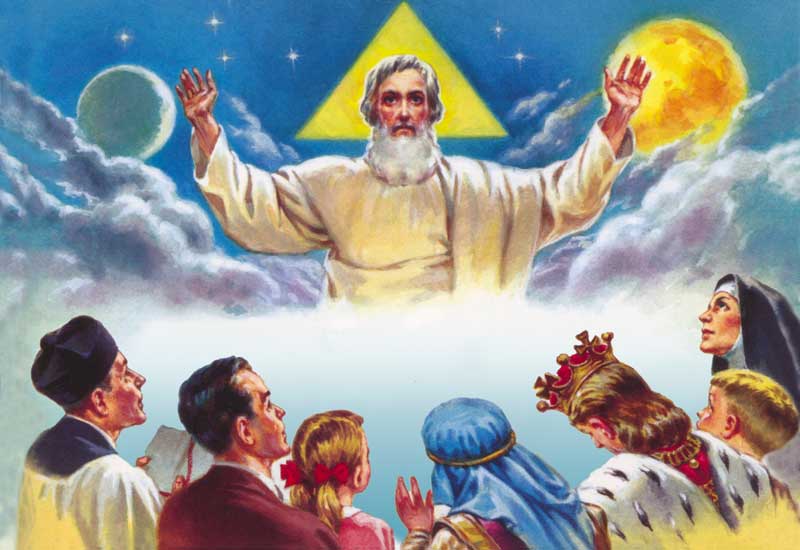

33. — What use does God want us to make of all created things?

34. — What are Angels?

35. — Do the Angels concern themselves with us?

36. — Has God given a Guardian Angel to each of us?
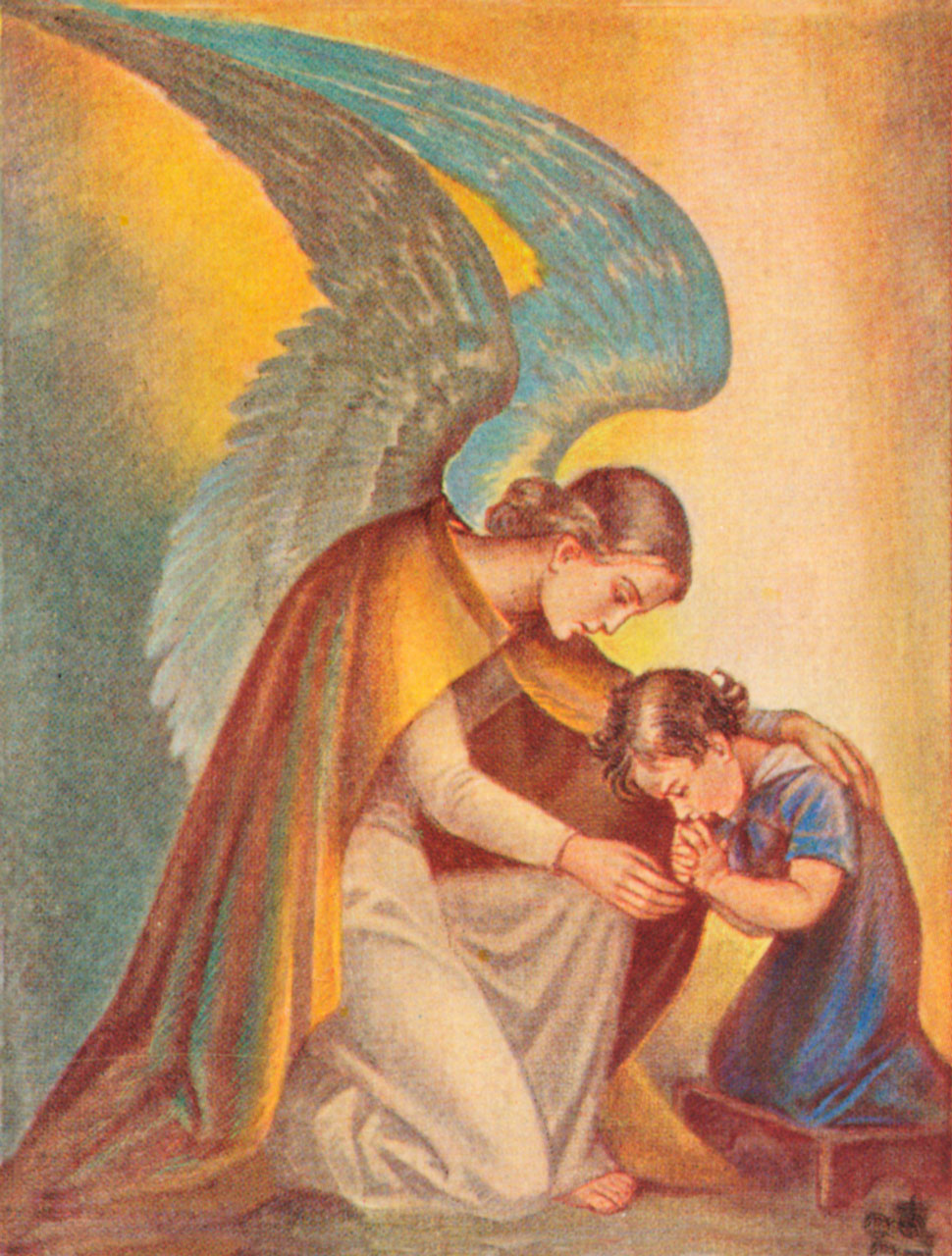

37. — What are our duties toward our Guardian Angel?

38. — Were the Angels, such as God created them, good and happy?
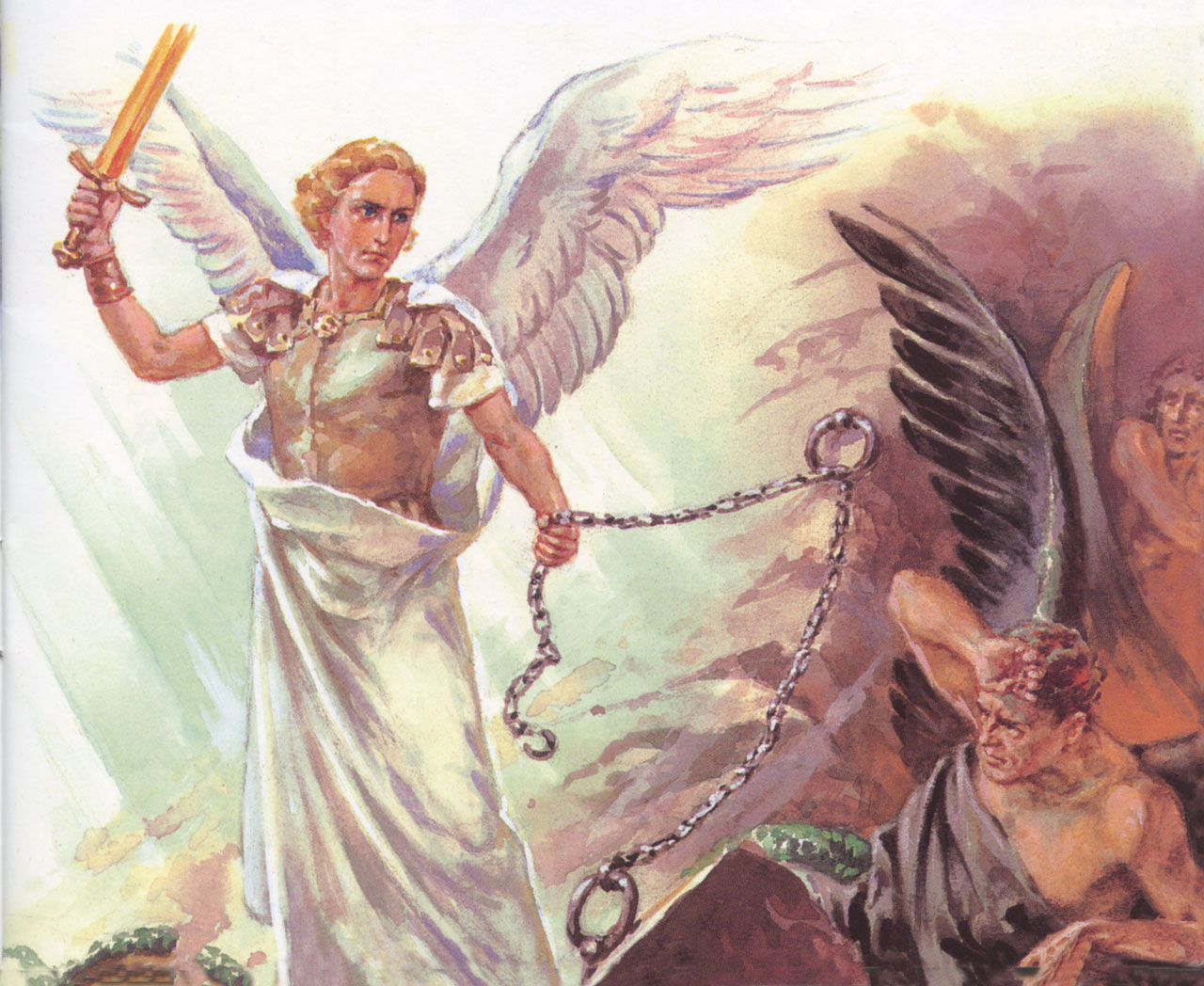

39. — Did all the Angels remain good and happy?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio de la leçon
Glossary
Angel: This word means “sent” or “messenger”. Angels are spirits, which means that they have no body.
Evil: Here the word “evil” means sin, which is the greatest of all evils. It can also mean illnesses and accidents which can affect us in our body or our mind, and which the Guardian Angels often ward off.
To respect the presence of our Guardian Angel: Do nothing wrong out of respect for our good Angel who assists us.
To show our gratitude to our Guardian Angel: Thank him for the good he does to us.
To invoke our Guardian Angel: Pray to him to come to our help in our needs of soul and body.
Temptation: The desire or thought of doing a bad, sinful thing. It becomes a sin when we consent to it.
Lesson 5: Our First Parents and their Fall
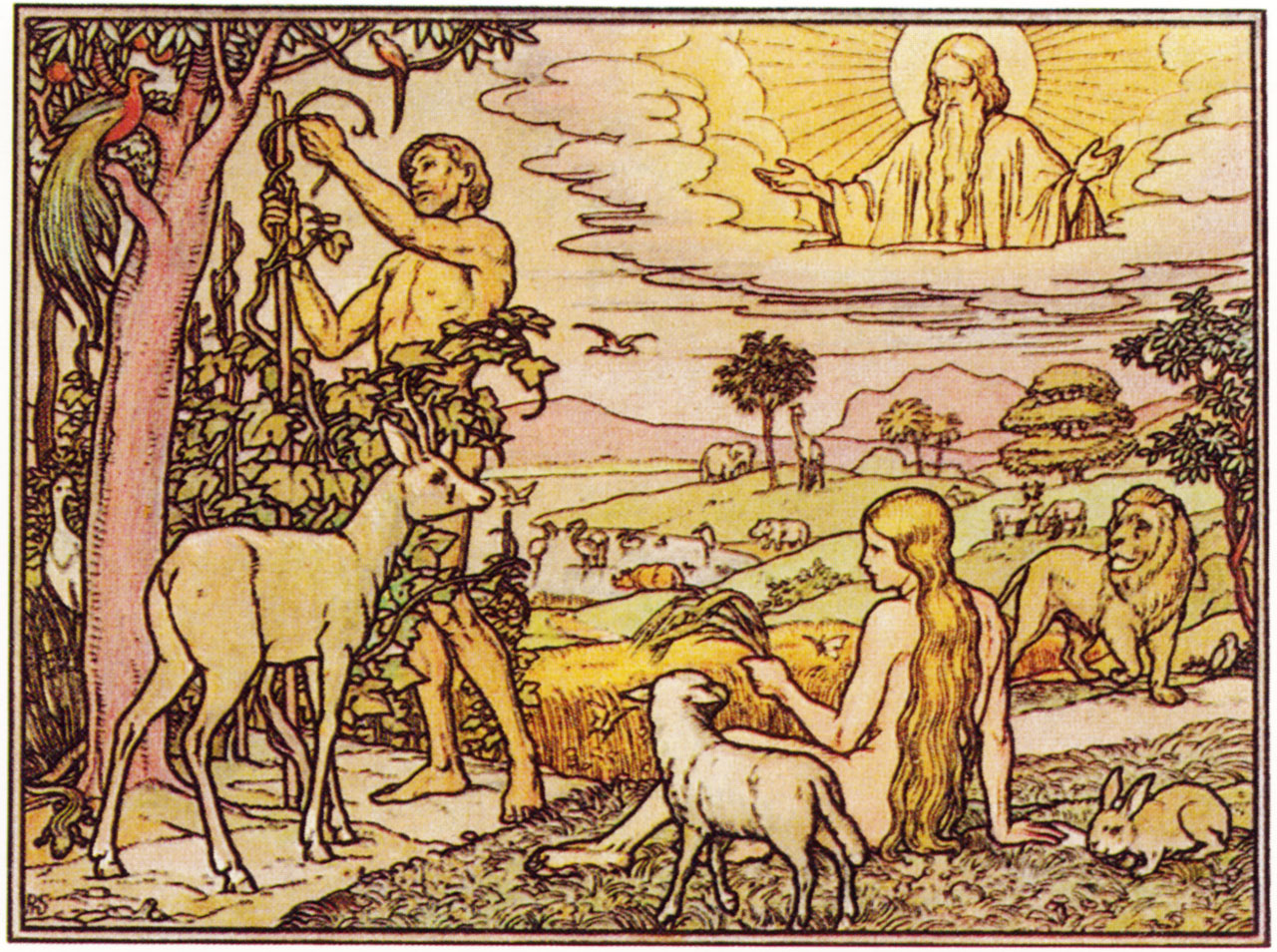

40. — Who were the first man and the first woman created by God?

41. — Do we all descend from Adam and Eve?
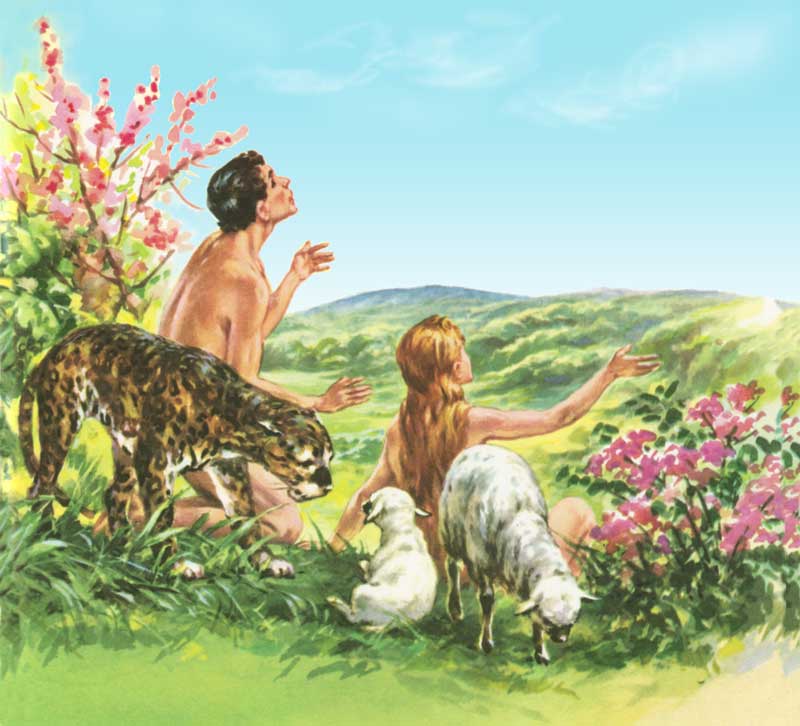

42. — Were Adam and Eve innocent and holy at the moment of their creation?

43. — What particular command did God give Adam and Eve to test their obedience?
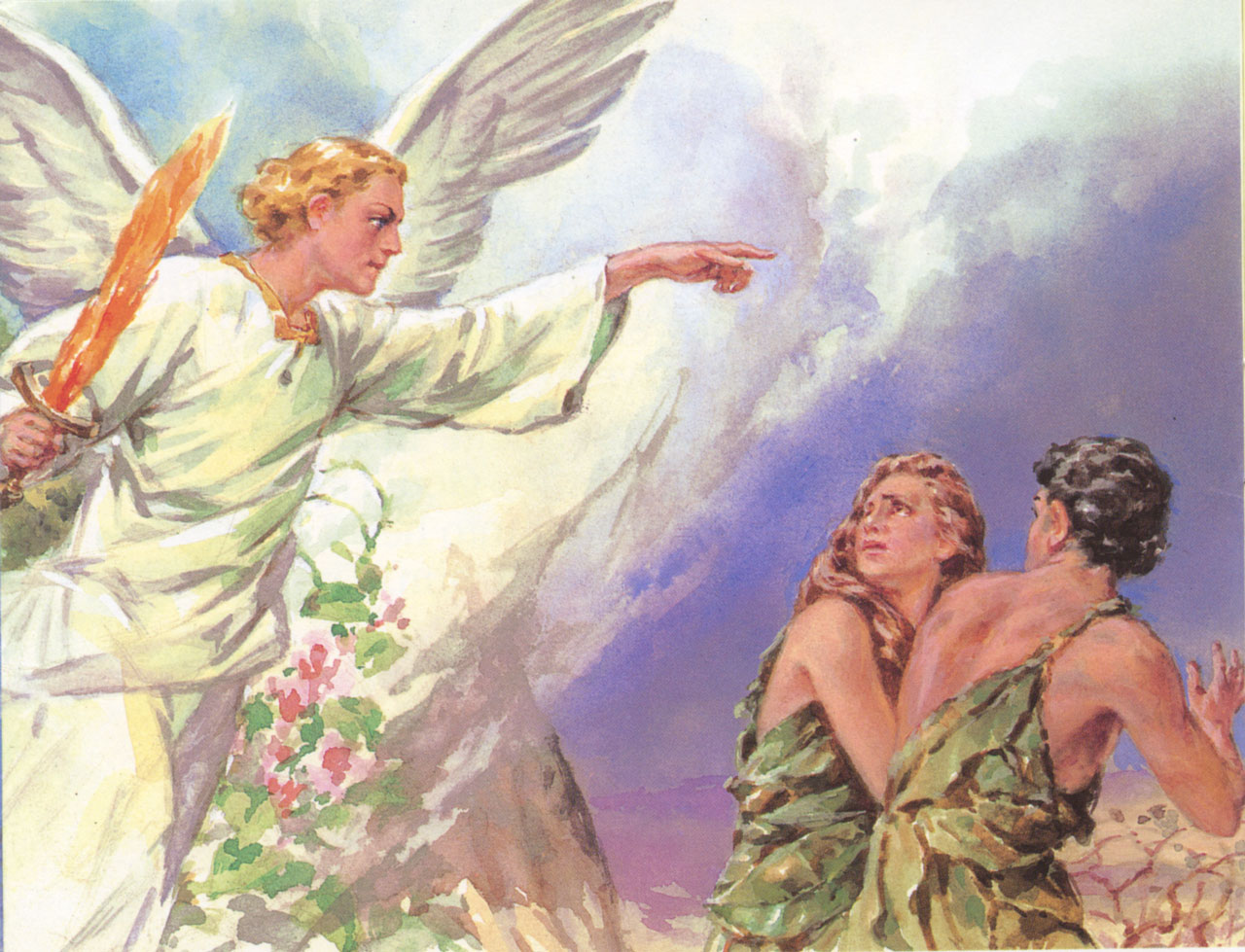

44. — How were Adam and Eve punished for their disobedience?

45. — What is the consequence for us of the sin of our first parents?
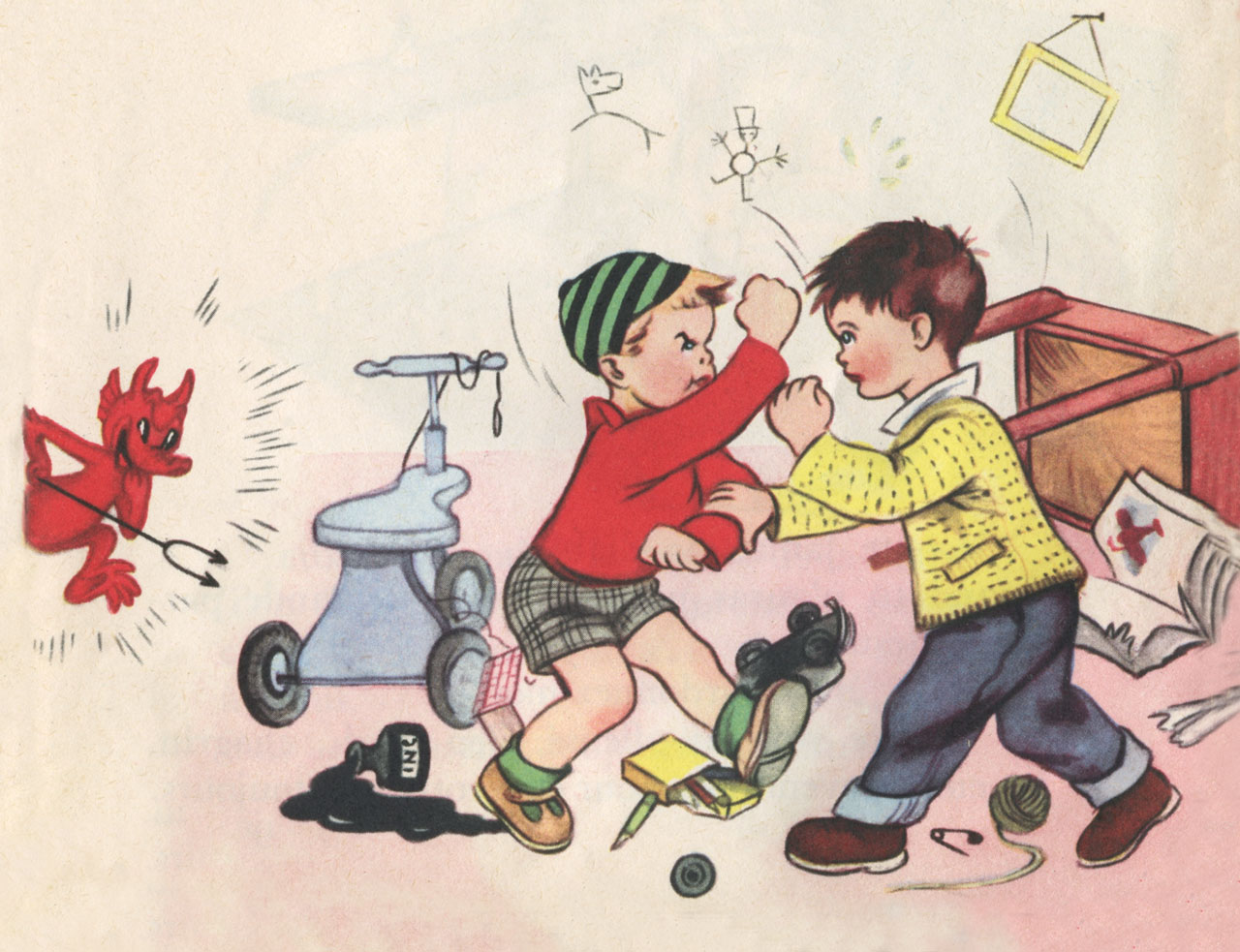

46. —Did the sin of our first parents darken our understanding and weaken our will?

47. — What do we call the sin of which all men are born guilty?

48. — Do the effects of original sin upon our understanding and our will remain in us after Baptism has cleansed us from original sin?

49. — Did God preserve anyone from original sin?
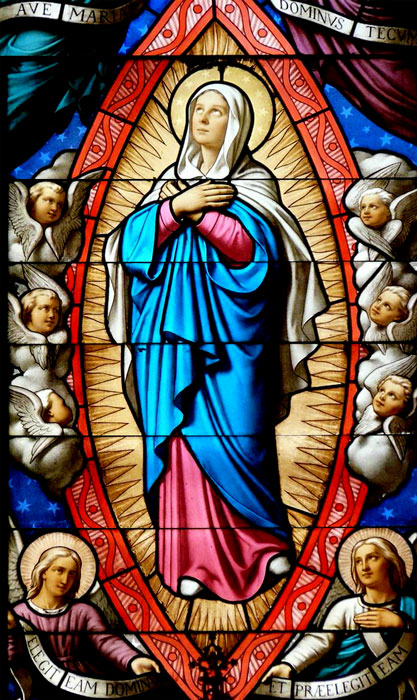

50. — What do we call this privilege of the Most Blessed Virgin Mary?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio de la leçon
Glossary
Adam: This name means “made of earth”.
Eve: This name means “mother of the living”.
Descendants: We are all descendants of Adam and Eve, meaning they are the ancestors of all human beings from the beginning of the world to the present day.
To test their obedience: God wanted to give Adam and Eve the opportunity to show the measure of their love for Him by being faithful and docile to His commands. God also wanted them to understand that they had a superior Master in Him, who had all rights over them.
Original: This word means “at the same time as our origin”, that is, at the beginning of Creation. This is how we may summarize the chastisements inflicted on Adam and Eve as punishment for their sin of pride, disobedience and insubordination:
1. They lost the state of grace and the privilege of being called children of God.
2. They were banished from earthly Paradise.
3. They were condemned to suffer and die.
4. They were condemned to transmit their sin and its evil consequences to all their children.
5. They lost order, that is, harmony in their intelligence, their will and their senses.
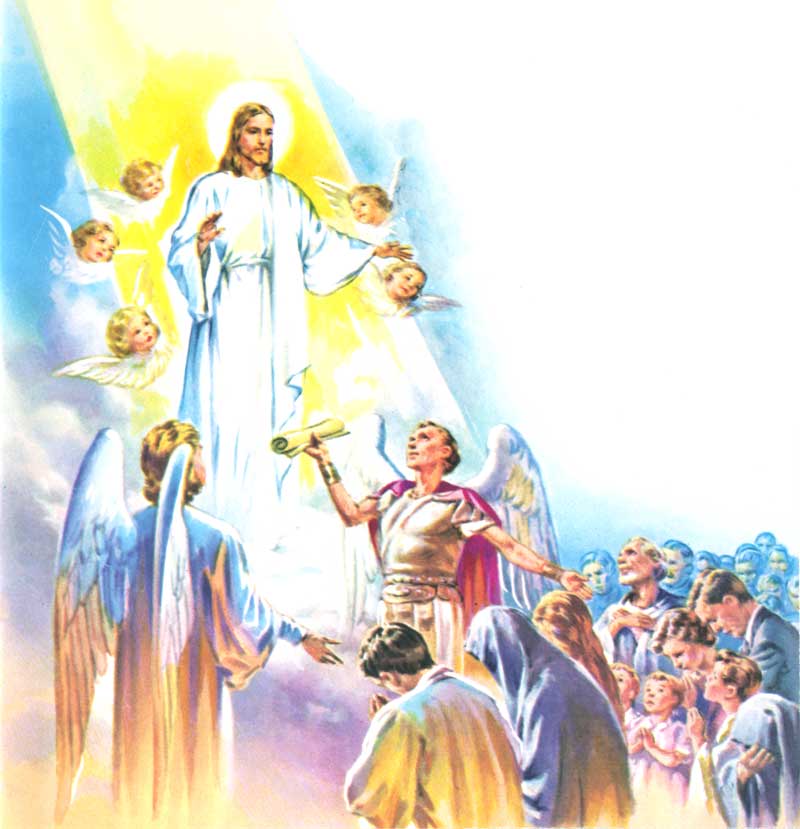
6. From the moment sin was committed, all human beings are inclined to evil.
Lesson 6: Sin and the different kinds of Sin

51. — What is sin?

52. — How many kinds of sin are there?

53. — How can we commit actual sin?

54. — How many kinds of actual sin are there?

55. — What is mortal sin?

56. — When is a sin mortal?

57. — What is the fate of the soul of a person who dies in the state of mortal sin?
58. — What is venial sin?

59. — What are the effects of venial sin?
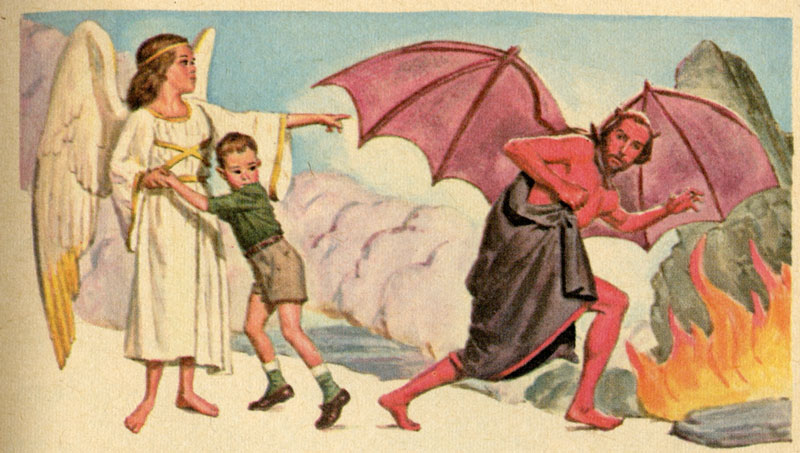

60. — Should we greatly dread venial sin?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio de la leçon
Glossary
Sin: Sin is any disobedience to God. It is necessarily a lack of love.
Mortal: The word mortal here means “death-dealing”. Saying that mortal sin gives death to the soul does not mean that a soul in the state of mortal sin is actually dead; our soul is immortal, so it cannot cease to live or exist. By this word, we understand that mortal sin deprives the soul of the state of grace and makes it incapable of performing meritorious works for Heaven, like a dead person who can no longer act on earth.
State of grace: Having no mortal sin in one’s soul. Living by the life of God; grace is the supernatural “life” of the soul.
Grave matter: Involving something very serious, an important point of the Law of God.
Light matter: A less important point of the Law of God.
With reflection: Knowing that what one is doing is very wrong.
With full consent of the will: Doing evil on purpose, though it is possible not to do it.
Age of reason: The age when one becomes capable of distinguishing between good and evil.
Sin of thought: A sin that takes place only in the mind without manifesting itself externally through actions – a thought of pride, jealousy, etc.
Sin of word: A sin that one commits by saying things which offend God and neighbor – lying, blasphemy, backbiting, etc.
Sin of deed: A sin that one commits by doing outwardly something which offends God and neighbor – injuring, killing, stealing, etc.
Sin of omission: A sin that one commits by not doing something which God commands – not loving one’s parents, not praying, not defending the rights of God, etc.
Lesson 7: The Capital Sins and opposed Virtues

61. — Name the seven capital sins, which are the principal sources of sin.

62. — What is pride?

63. — What is the virtue opposed to pride?

64. — What is covetousness?

65. — Covetousness is an inordinate attachment to earthly goods, and chiefly to money.

66. — What is lust?

67. — What is the virtue opposed to lust?

68. — What is envy?

69. — What is the virtue opposed to envy?
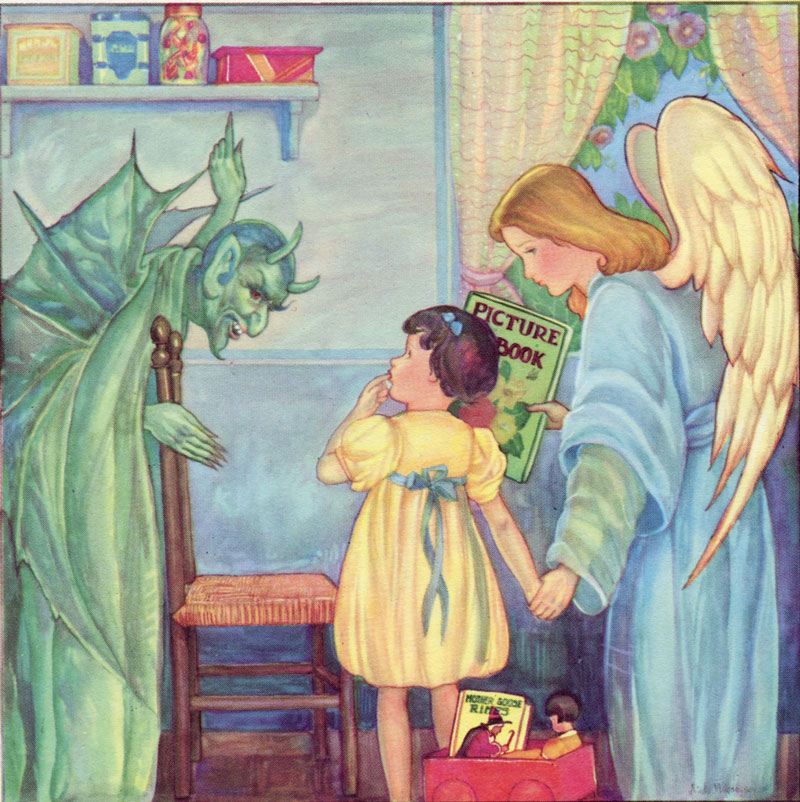

70. — What is gluttony?

71. — What are the most dangerous kinds of gluttony?

72. — What are the sins ordinarily caused by drunkenness and drug abuse?

73. — What are the virtues opposed to gluttony?

74. — What is anger?

75. — What are the virtues opposed to anger?

76. — What is sloth?

77. — What are the virtues opposed to sloth?

78. — What are the means to take against temptations?
The means to take against temptations are:
1. Vigilance and avoidance of dangerous occasions, especially bad company.
2. Prayer, and frequent confession and Communion.
3. Remembrance of our last ends.
4. Openness of soul to a good director.
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio of the Lesson
Glossary
Capital: The term “capital” given to each of these sins does not mean that these sins are in themselves more serious than the others. By this word, which means “head” or “chief”, we understand that a capital sin is one which leads to other sins.
Lesson 8: The Incarnation and the Redemption

79. — Did God abandon man after his fall into sin?

80. — Who is this Redeemer promised by God to the human race?

81. — Who is Our Lord Jesus Christ?

82. — Why do we say that Jesus Christ is true God?

83. — Why do we say that Jesus Christ is true man?
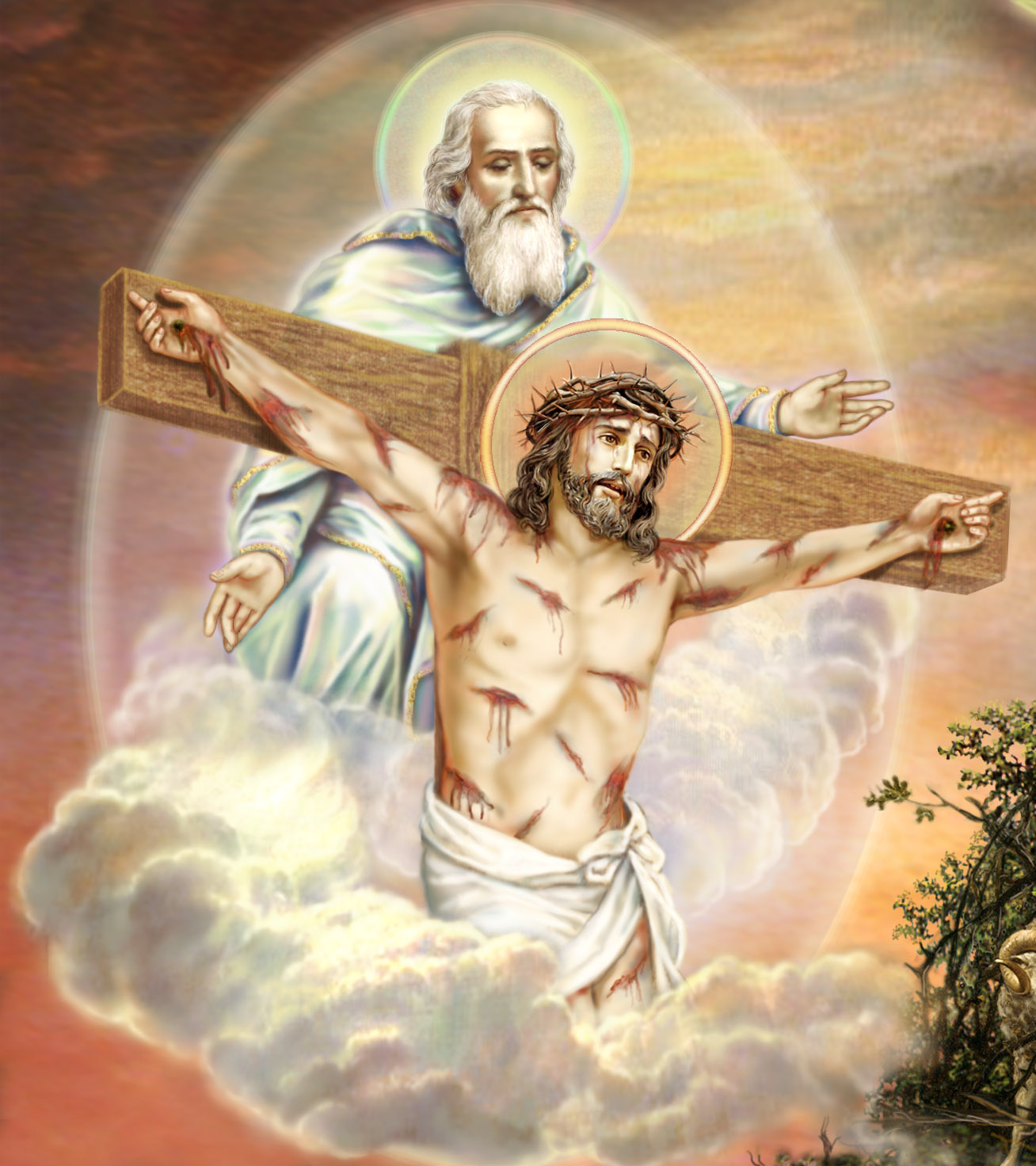

84. — Why do we say that Jesus Christ is Our Lord?

85. — Are there two natures in Jesus Christ?

86. — Are there several persons in Jesus Christ?

87. — Was Jesus Christ always God?

88. — Was Jesus Christ always man?

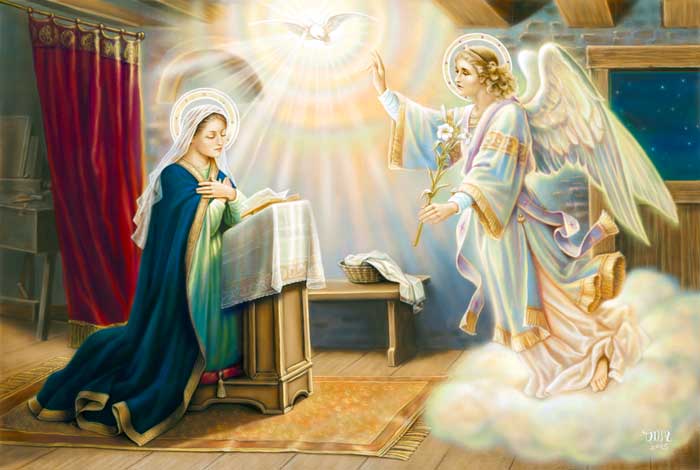
89. — What is the mystery of the Incarnation?
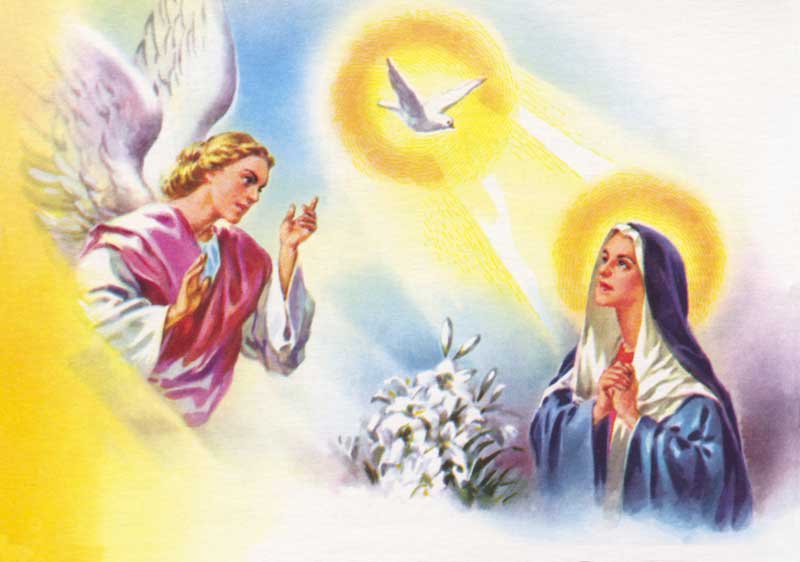

90. — How was the mystery of the Incarnation effected?

91. —Is the Most Blessed Virgin truly the Mother of God?

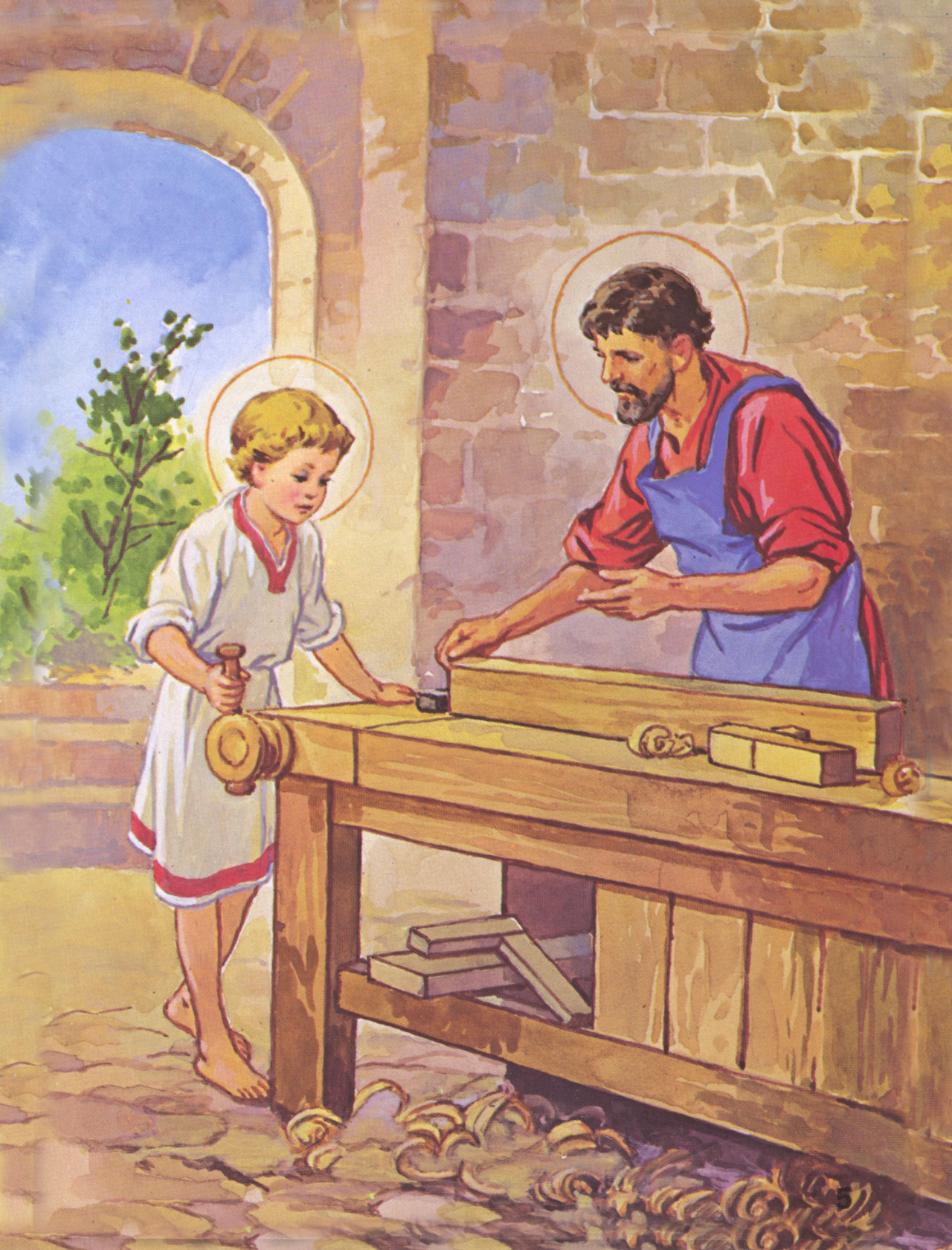
92. — Who was the foster father of Our Lord Jesus Christ?

93. — Why did the Son of God become man?

94. — Did the Son of God become man immediately after the sin of our first parents?

95. — How could those who lived before the Incarnation of the Son of God be saved?

96. — On what day did the Son of God become man?

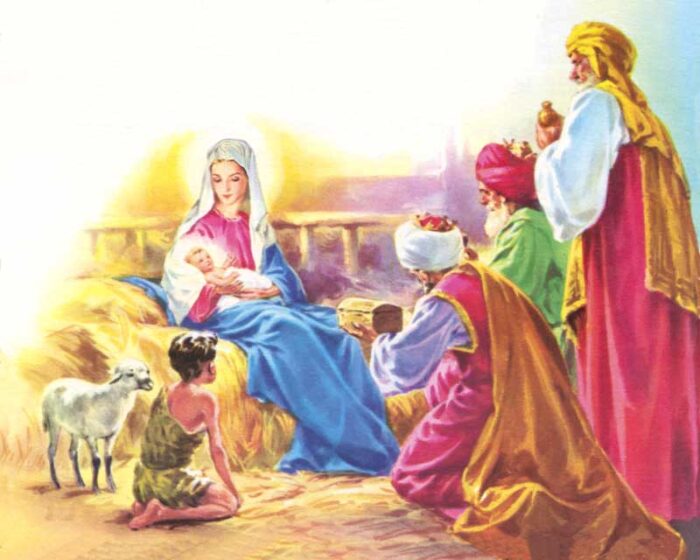
97. — On what day and where was Jesus Christ born?

98. — Why did Jesus Christ remain thirty-three years on earth?

99. — What is the meaning of the word Gospel?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio of the Lesson
Glossary
Incarnation: This term comes from two Latin words which mean “in the flesh”.
Miracle: A sensible phenomenon which is beyond the power of nature and which only God can do.
Bethlehem: This name means “House of Bread”.
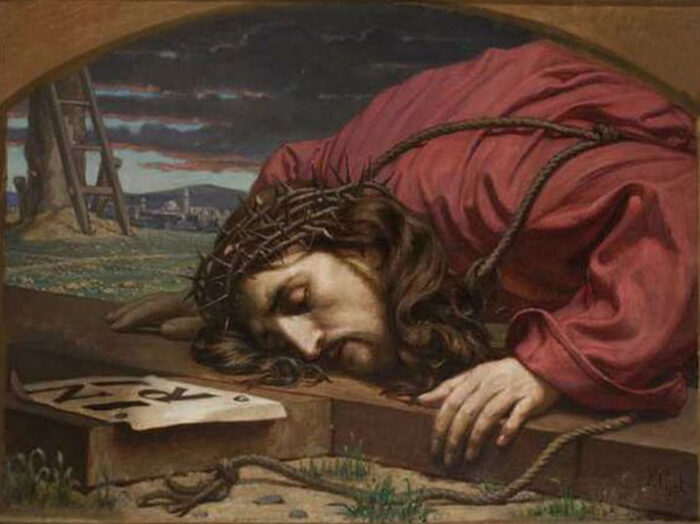
Lesson 9: The Passion, Death, Resurrection and Ascension of Our Lord

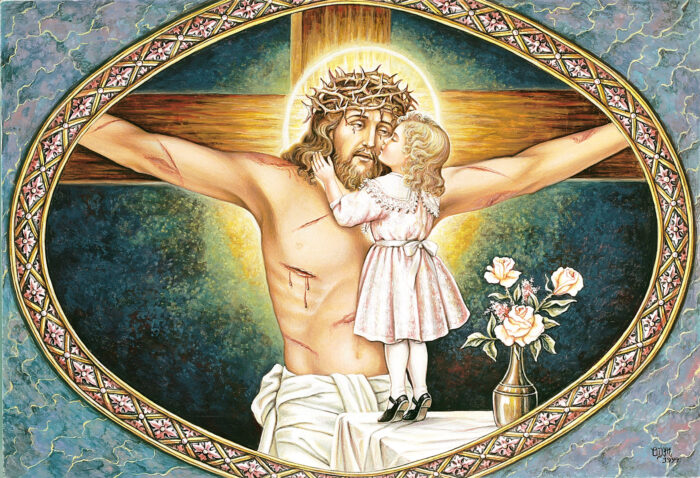
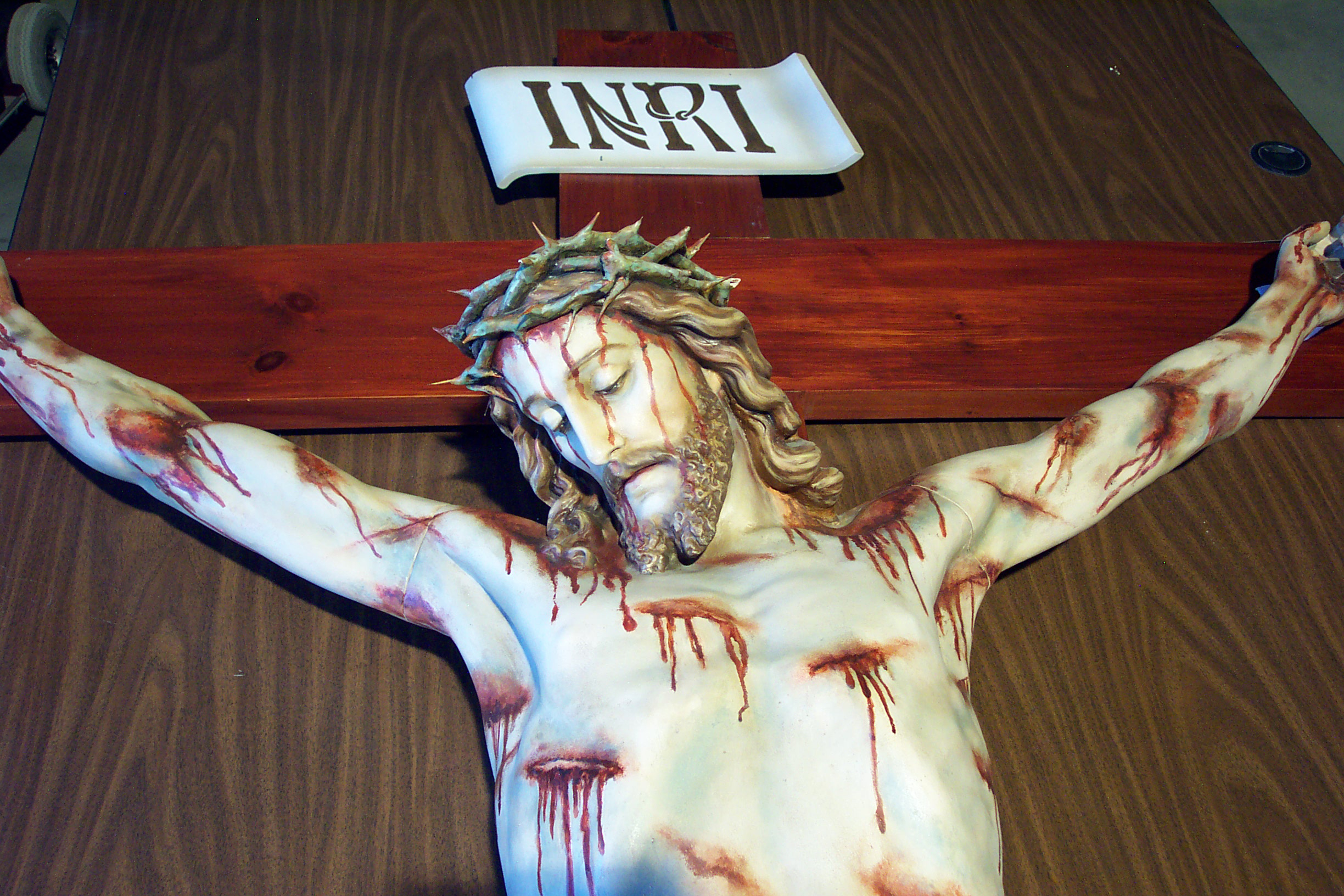
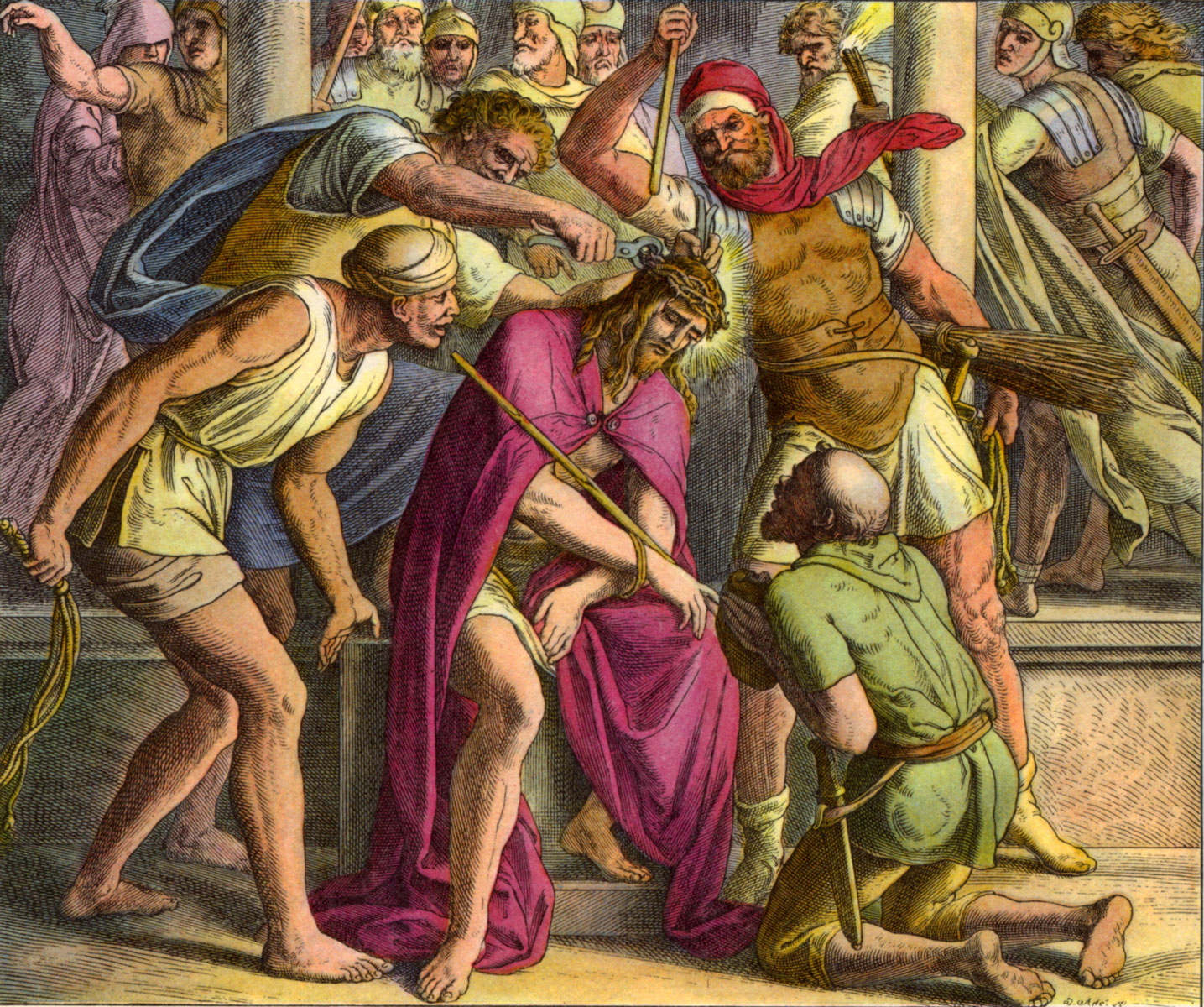
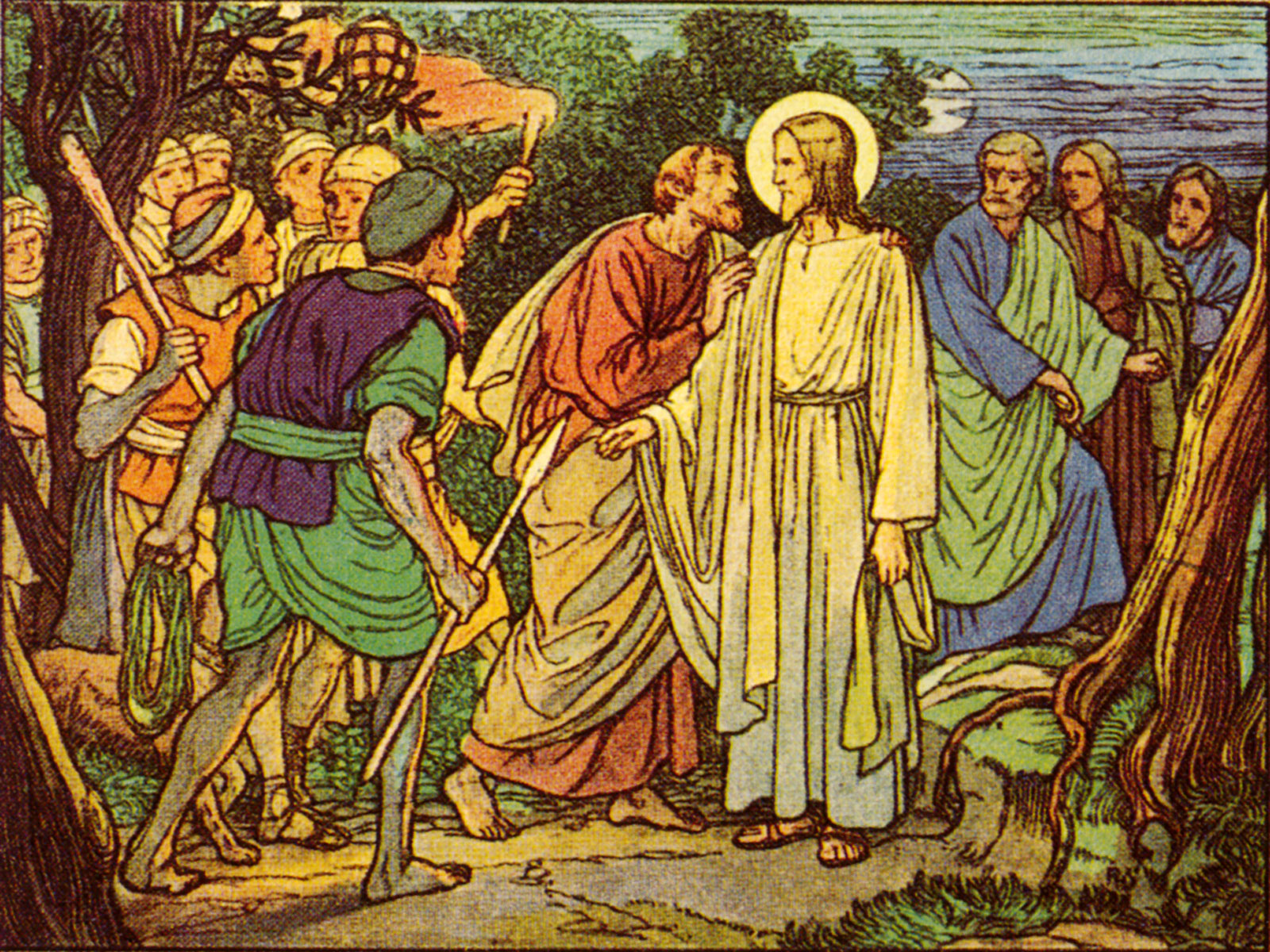
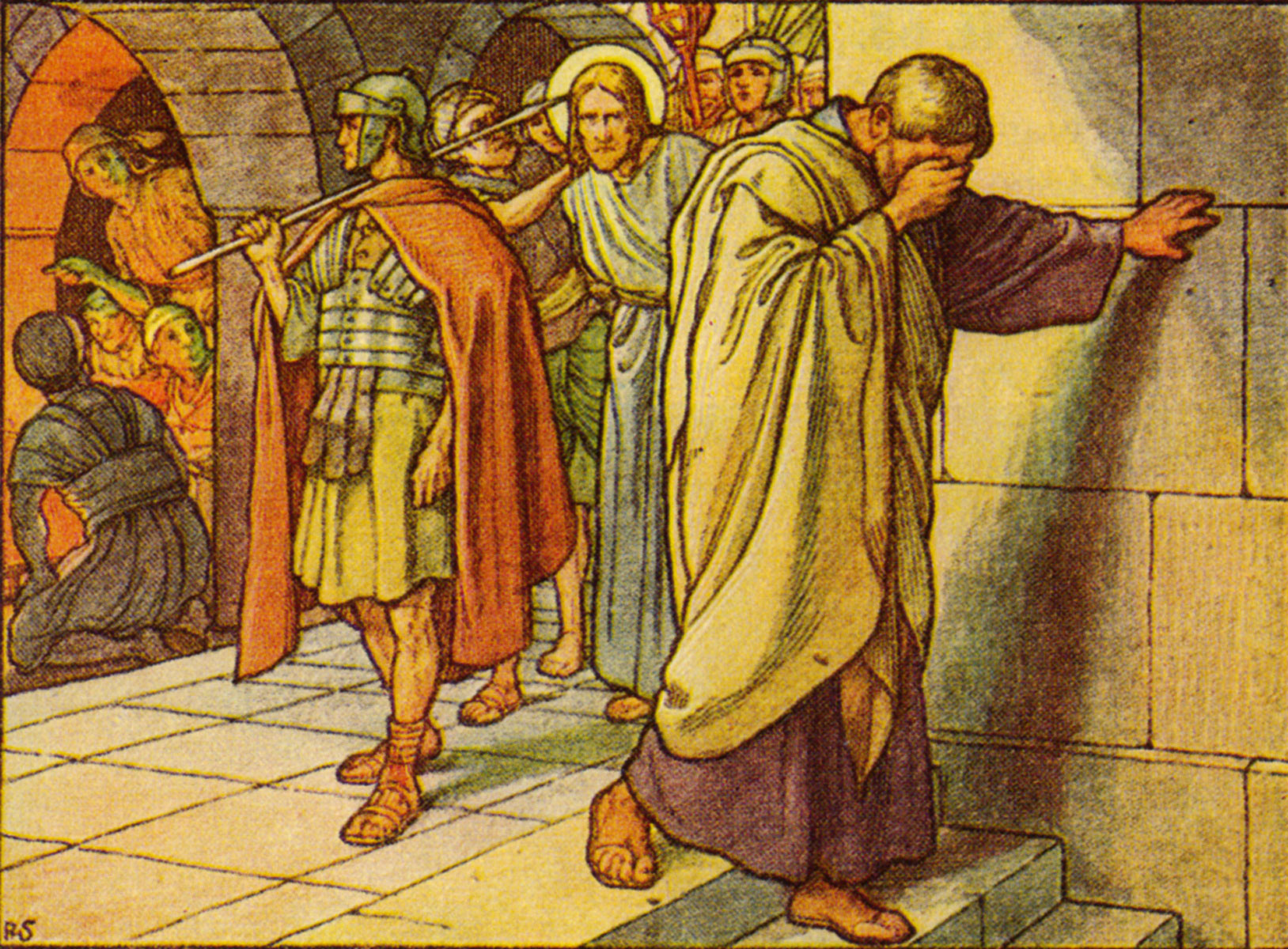
100. — What did Jesus Christ suffer for us?

101. — What day did Jesus Christ die?

102. — Why do we call good the day on which Jesus Christ died such a cruel death?
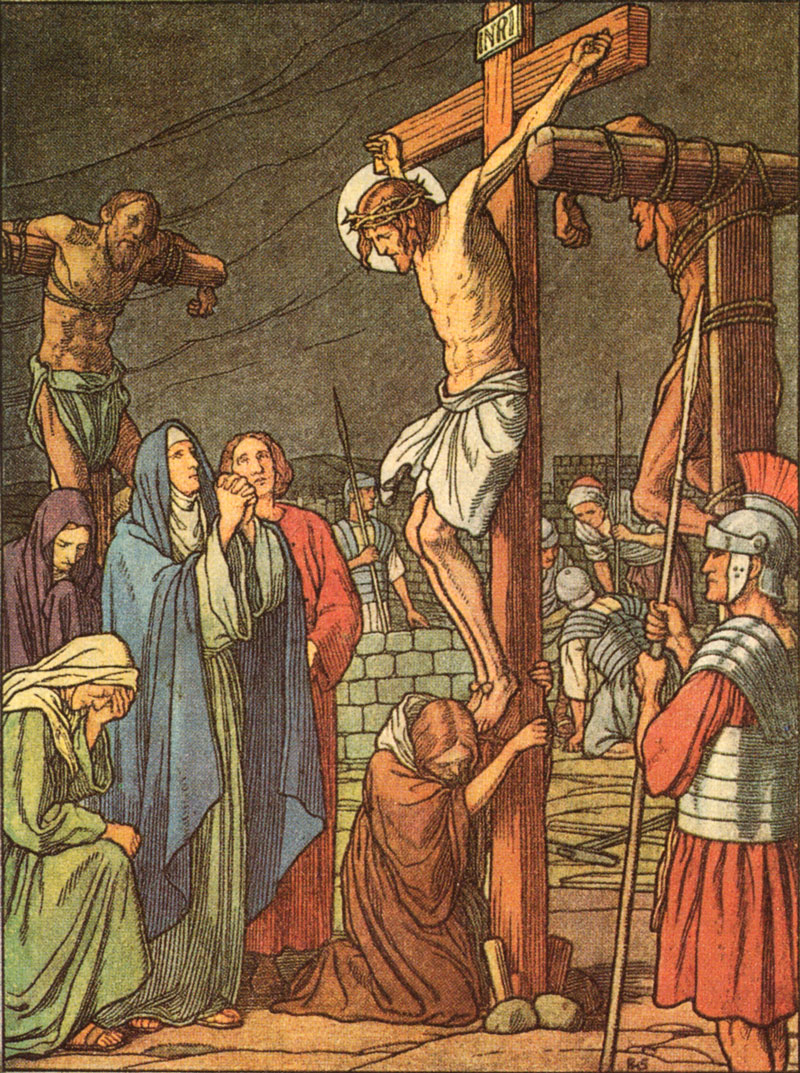
103. — Where and how did Jesus Christ die?
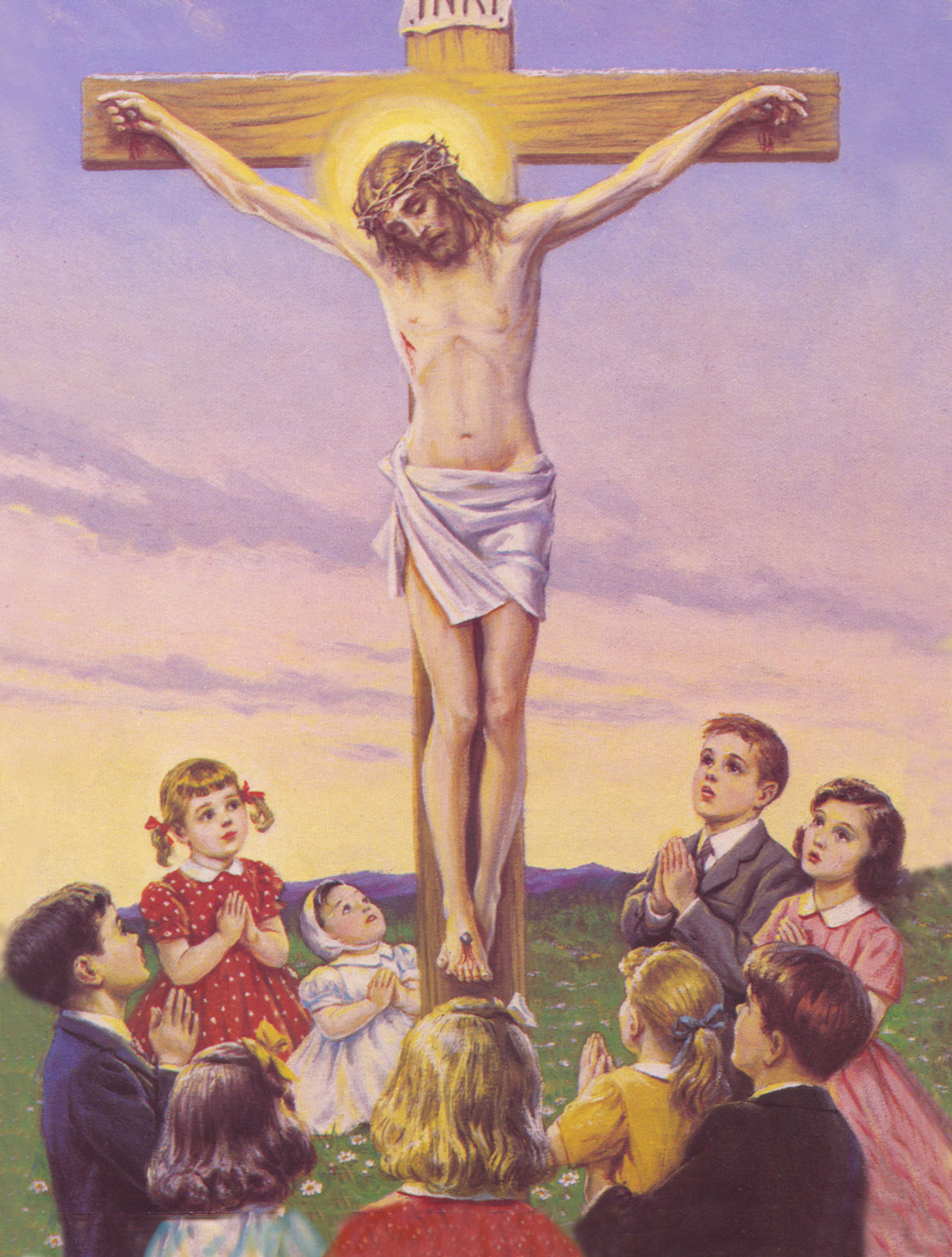

104. — Why did Jesus Christ die?

105. — How did Jesus Christ redeem us?

106. — What lessons do we learn from the sufferings and death of Jesus Christ?
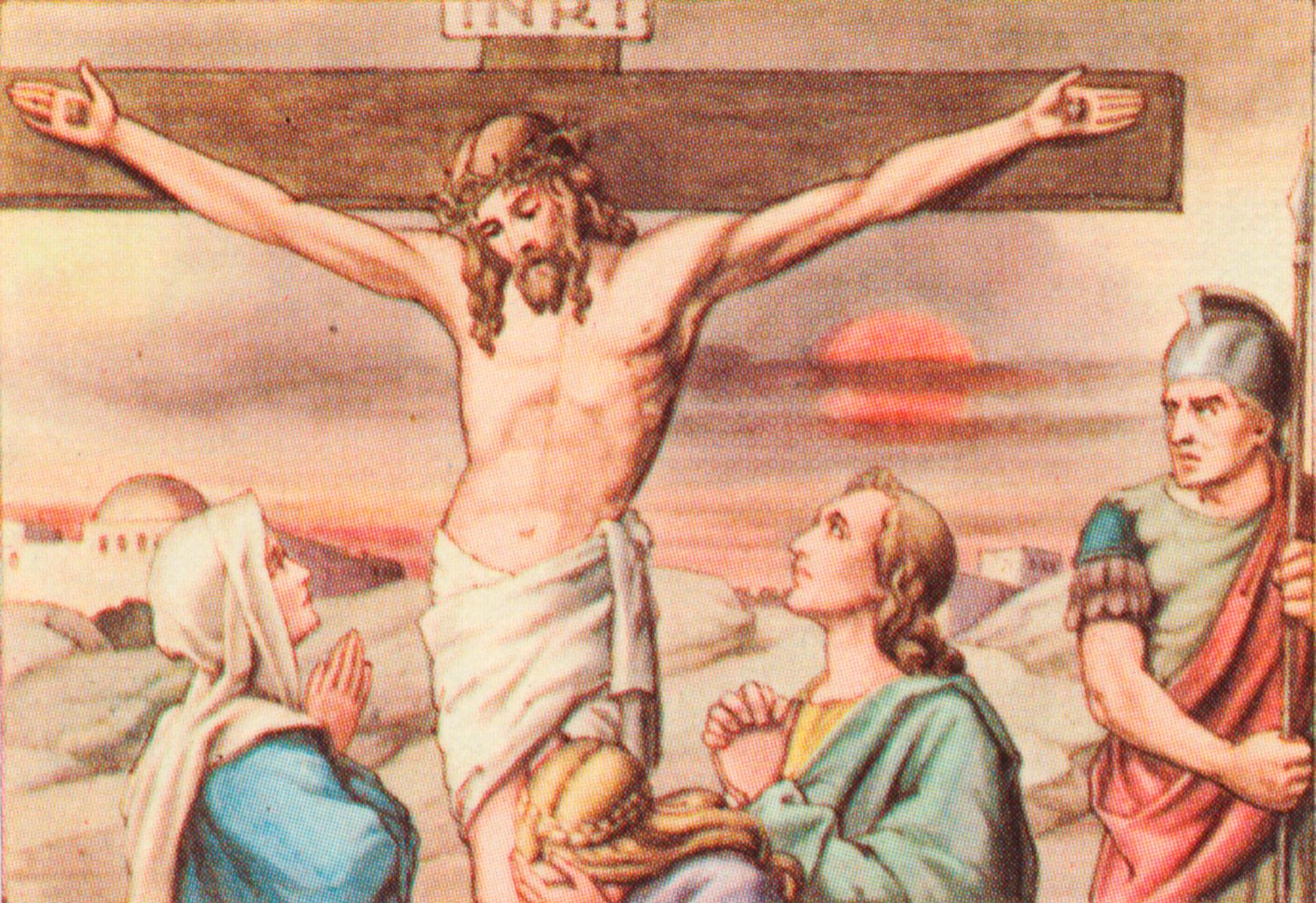
107. — What do we call the mystery of the death of Jesus Christ on the cross for us?

108. — What became of the soul of Jesus Christ after His death?
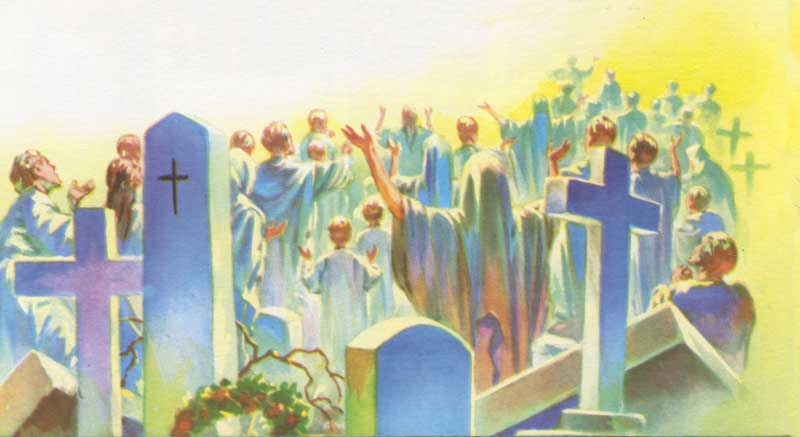

109. — Why did Jesus Christ descend into limbo?

110. — Where was the body of Jesus Christ while His soul was in limbo?
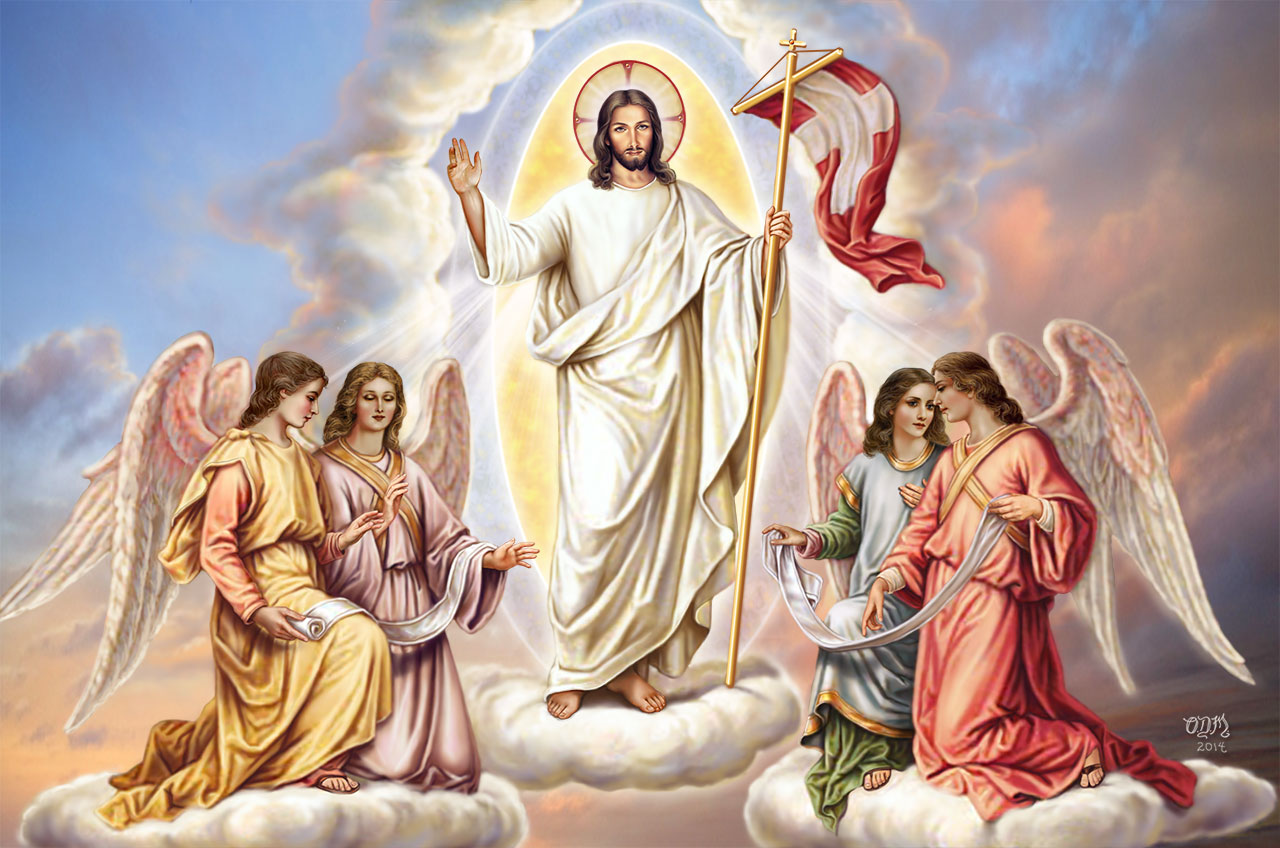

111. — What day did Jesus Christ rise from the dead?

112. — How did Jesus Christ rise from the dead?

113. — How long did Jesus Christ remain on earth after His Resurrection?
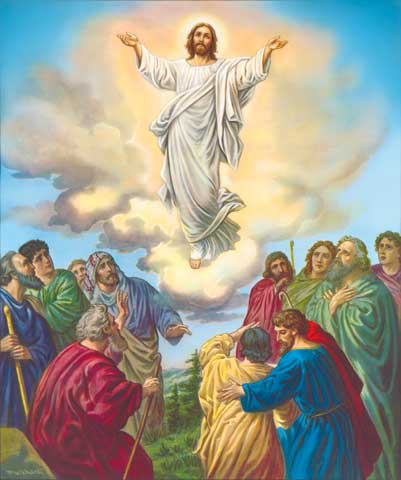

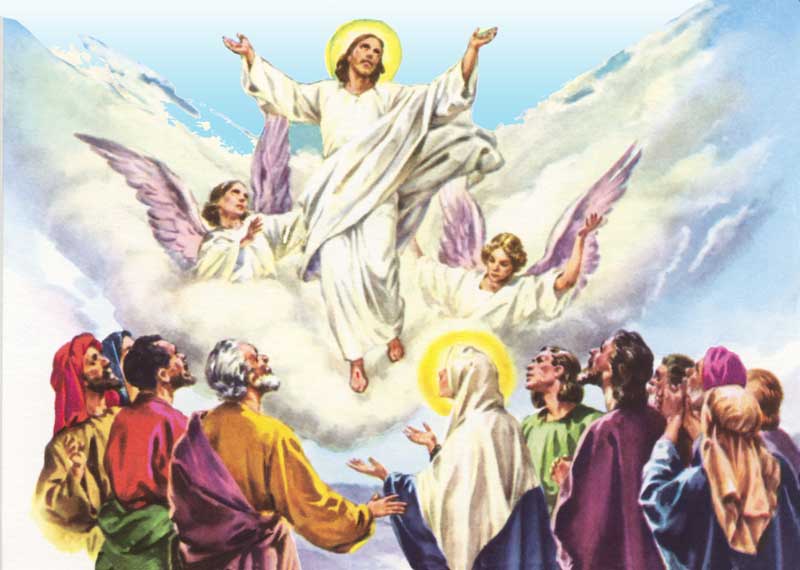
114. — What did Jesus Christ do on the fortieth day after His Resurrection?

115. — Where is Jesus Christ in Heaven?

116. — What do we mean by the words: Sitteth at the right hand of God, the Father Almighty?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio of the Lesson
Glossary
Agony of Jesus: This is the sorrowful state in which He found Himself in the Garden of Olives, also called the Garden of Gethsemani.
Garden of Olives: A garden or grove planted with olive trees near the city of Jerusalem.
Opprobrium: Insults, offenses, coarse remarks, indignities, abuse. Covered with opprobrium means to receive countless insults, etc.
Scourging: Flogging, beating with whips or rods.
Descended into hell: This does not refer to the place inhabited by the demons and the damned. Here the term hell refers to the lower parts of the earth (inferi in Latin), also called limbo (in Latin edge, meaning “the edge of hell”), where the souls of the Just who died before Jesus Christ awaited the grace of redemption. By His suffering and death, Christ reopened the gates of Heaven, into which He brought the souls of the Just.
Resurrected: Having come back from death to life; risen.
Pasch: Derived from a word meaning passage. The Jews celebrated the Pasch, or Passover, in remembrance of the passage of the Exterminating Angel which was the sign of their deliverance from captivity. The Apostles established the Christian feast of Easter (called Pascha in Aramaic) in remembrance of the Resurrection of our Lord Jesus Christ, of His passage from death to life, the sign of our salvation. Jesus Christ rose on the third day: Not three days after His death. Resurrected by His almighty power: Our Lord resurrected Himself without needing anyone, because He is God Almighty.
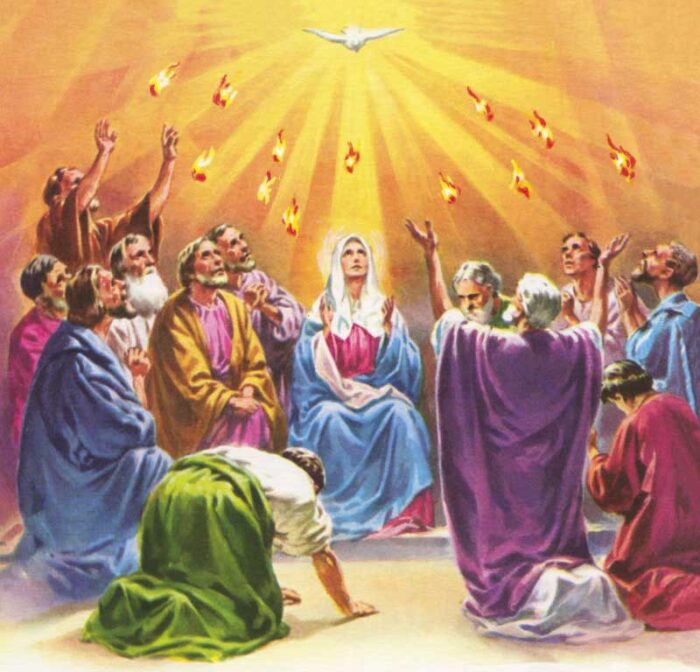
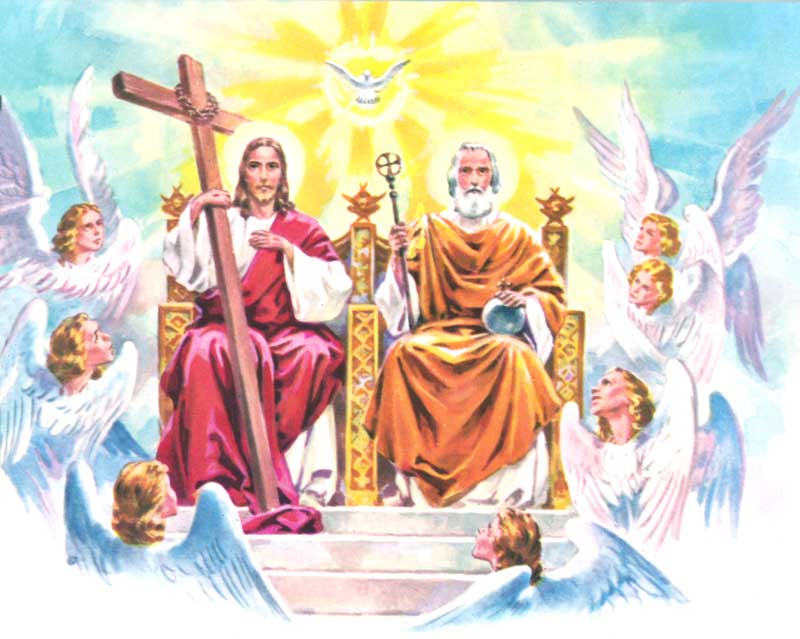
Lesson 10: The Holy Spirit, His Descent upon the Apostles

117. — Who is the Holy Ghost, or Holy Spirit?

118. — From whom does the Holy Spirit proceed?

119. — Is the Holy Spirit equal to the Father and the Son?
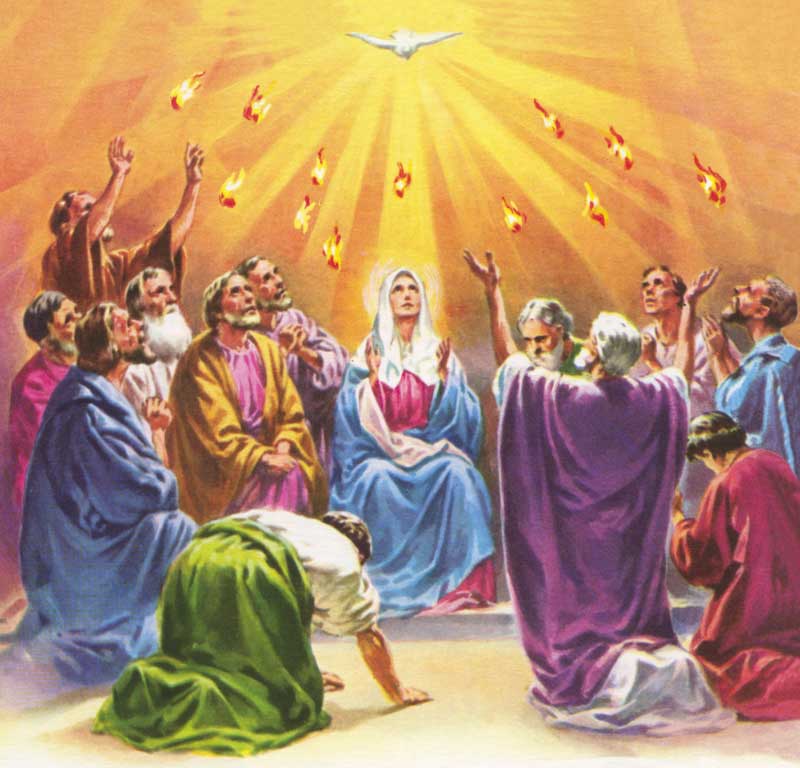

120. — What day did the Holy Spirit come down upon the Apostles?

121. — In what form did the Holy Spirit come down upon the Apostles?

122. — Who sent the Holy Spirit upon the Apostles?
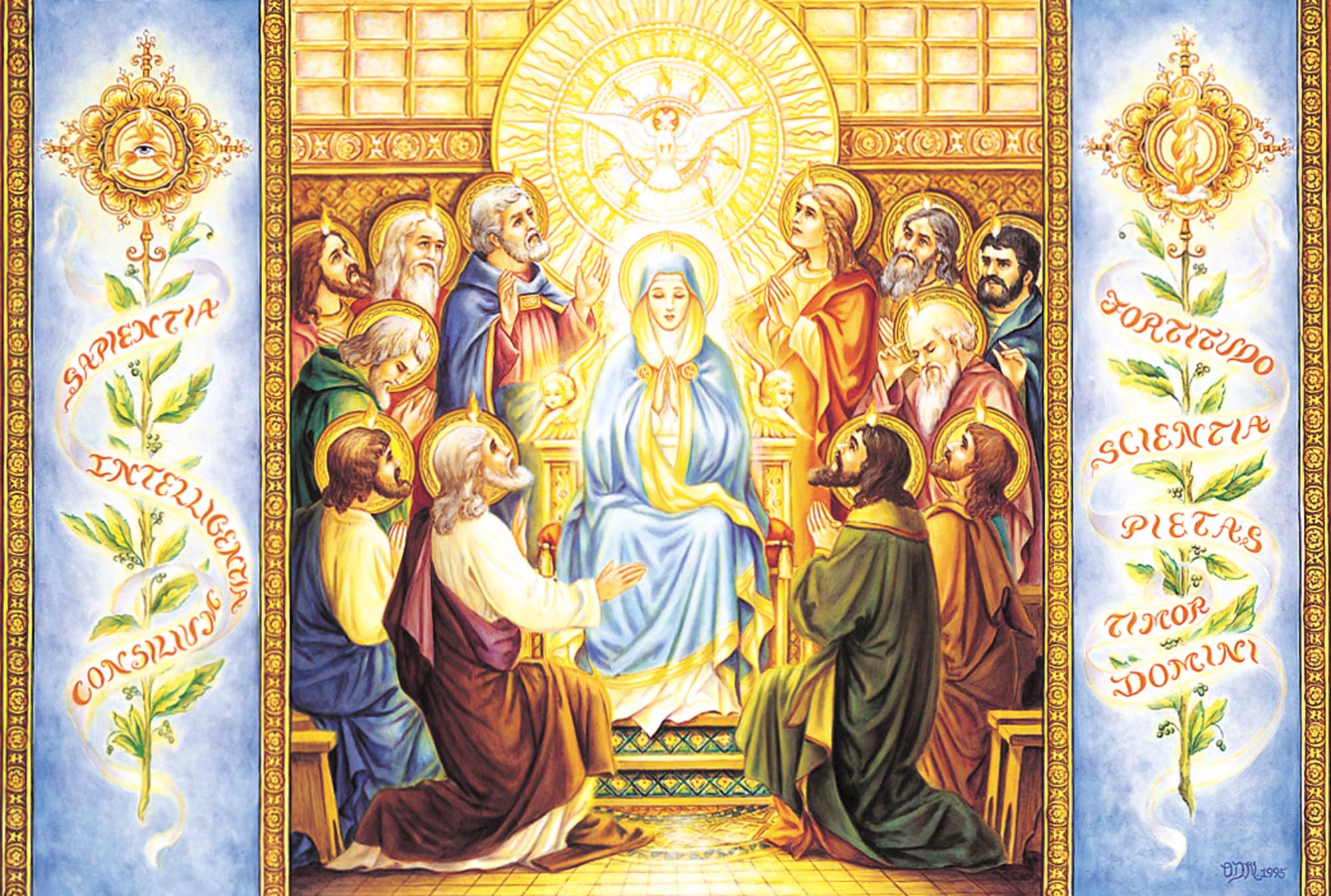

123. — Why was the Holy Spirit sent upon the Apostles?

124. — Will the Holy Spirit abide with the Church forever?

125. — Does the Holy Spirit also communicate Himself to us?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio of the Lesson
Glossary
Proceed from: To “come from”.
Pentecost: Derived from a Greek word meaning “fiftieth”. This term was given to the day of the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the Blessed Virgin and the Apostles because that event took place fifty days after the Resurrection of Our Lord.
Strengthen the Apostles: The Holy Spirit increased (strengthened) the courage of the Apostles, because before they received the Holy Spirit, the Apostles were fearful and cowardly. After the death of Jesus they had remained hidden for fear of being mistreated and put to death like their Master.
Sanctify the Church: The Holy Spirit endowed the Apostles with the grace of moving men to love the virtues taught by Our Lord which sanctify them, make them holy.
Lesson 11: The Effects of the Redemption

126. — What is the mystery of the Redemption?

127. — What are the chief effects of the Redemption?
The chief effects of the Redemption are:
1. The satisfaction made to divine justice for our sins, by the sufferings and death of Jesus Christ.
2. The gaining of grace for men.

128. — What is grace?

129. — How many kinds of grace are there?
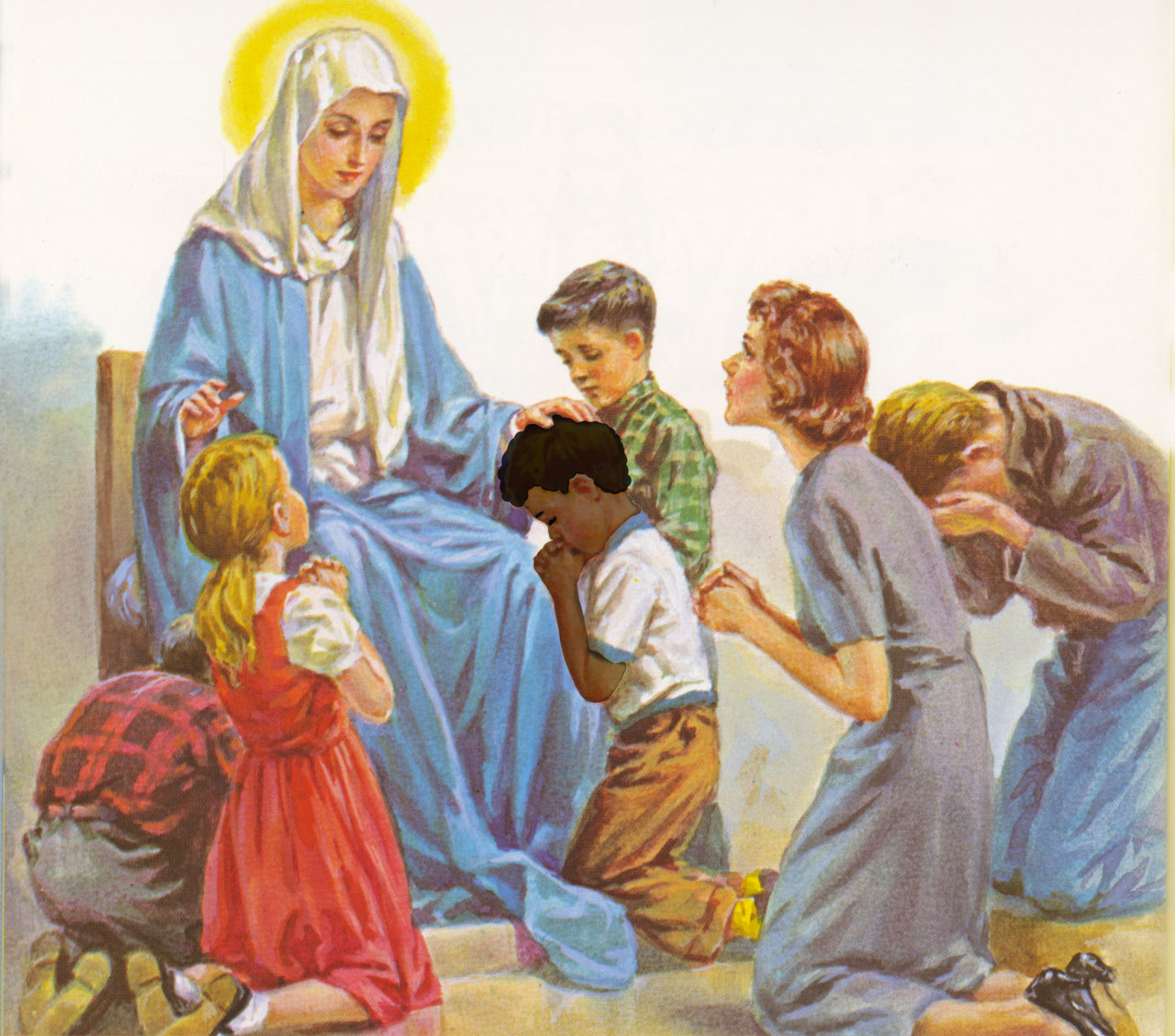

130. — What is sanctifying grace?

131. — When do we receive sanctifying grace for the first time?

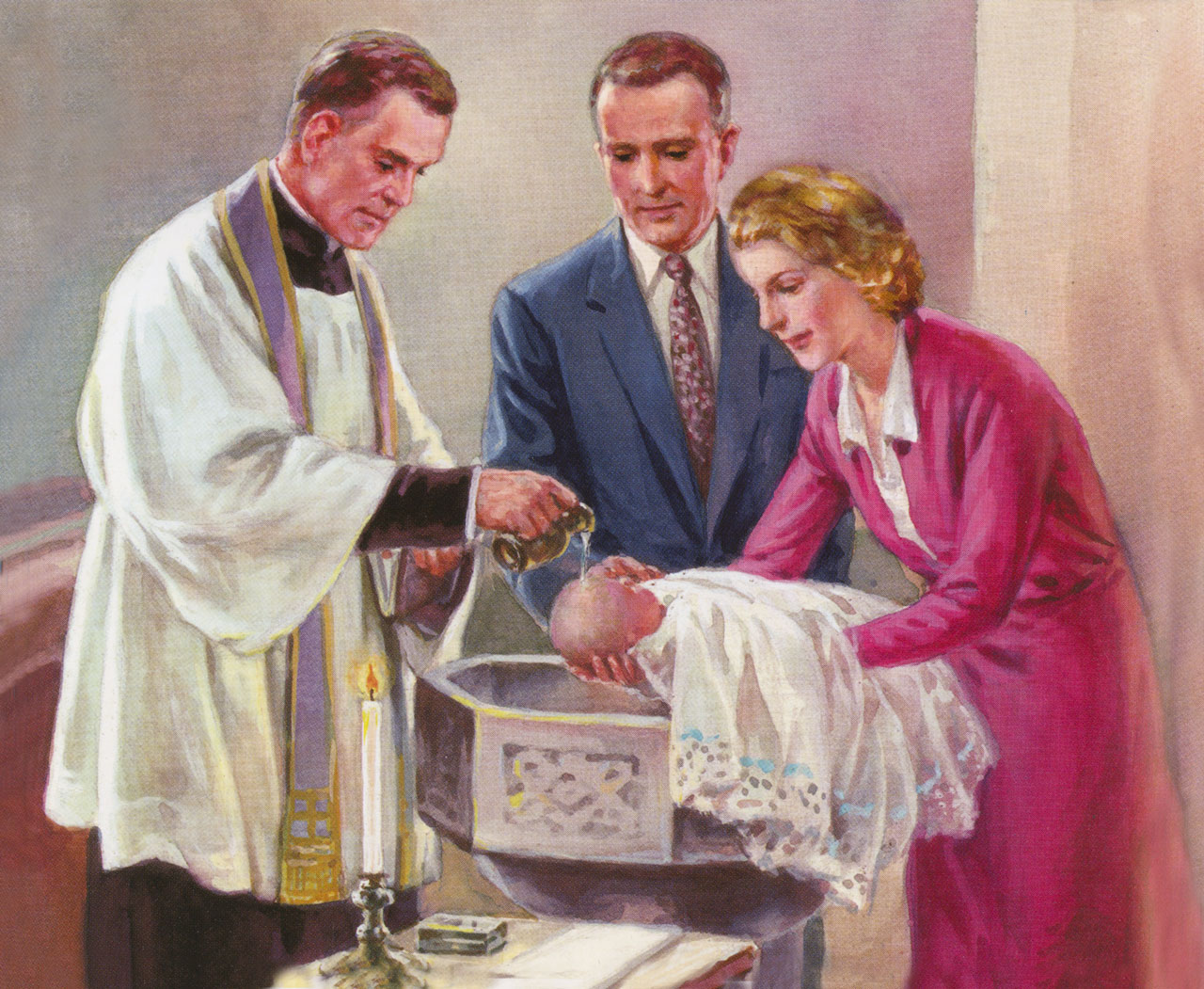
132. — Can we lose sanctifying grace?

133. — What is actual grace?

134. — Is grace necessary for salvation?

135. — Can we resist the grace of God?

136. — What is the grace of perseverance?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio of the Lesson
Glossary
Virtue: from the Latin “vir”, which means “energetic man”. Virtue is a good disposition of the soul acquired often by great efforts, which becomes a healthy habit of our heart, and inspires our actions, attitudes, reactions. It is in the trial that true virtue manifests itself.
Grace: from the Latin “gratia” which means “favor”. Grace is a free gift that God gives us; we do not deserve it.
Lesson 12: The Effects of the Redemption (cont.) - The Theological Virtues

137. — Which virtues does God infuse into the soul with sanctifying grace?

138. — Why are these three virtues called theological or divine?
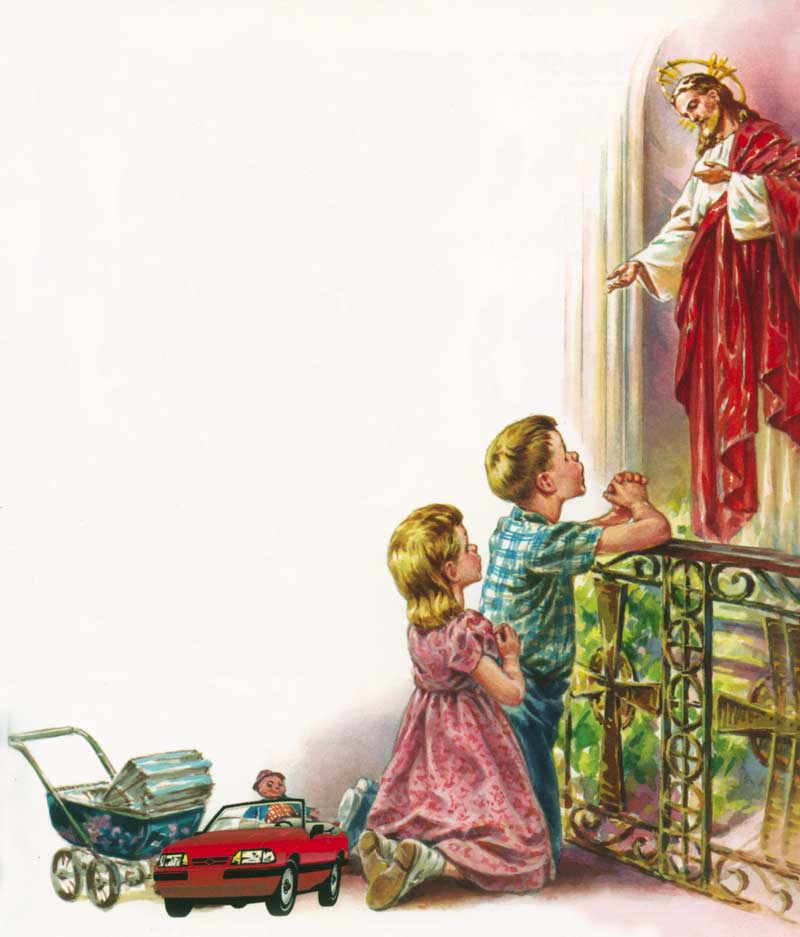

139. — What is faith?
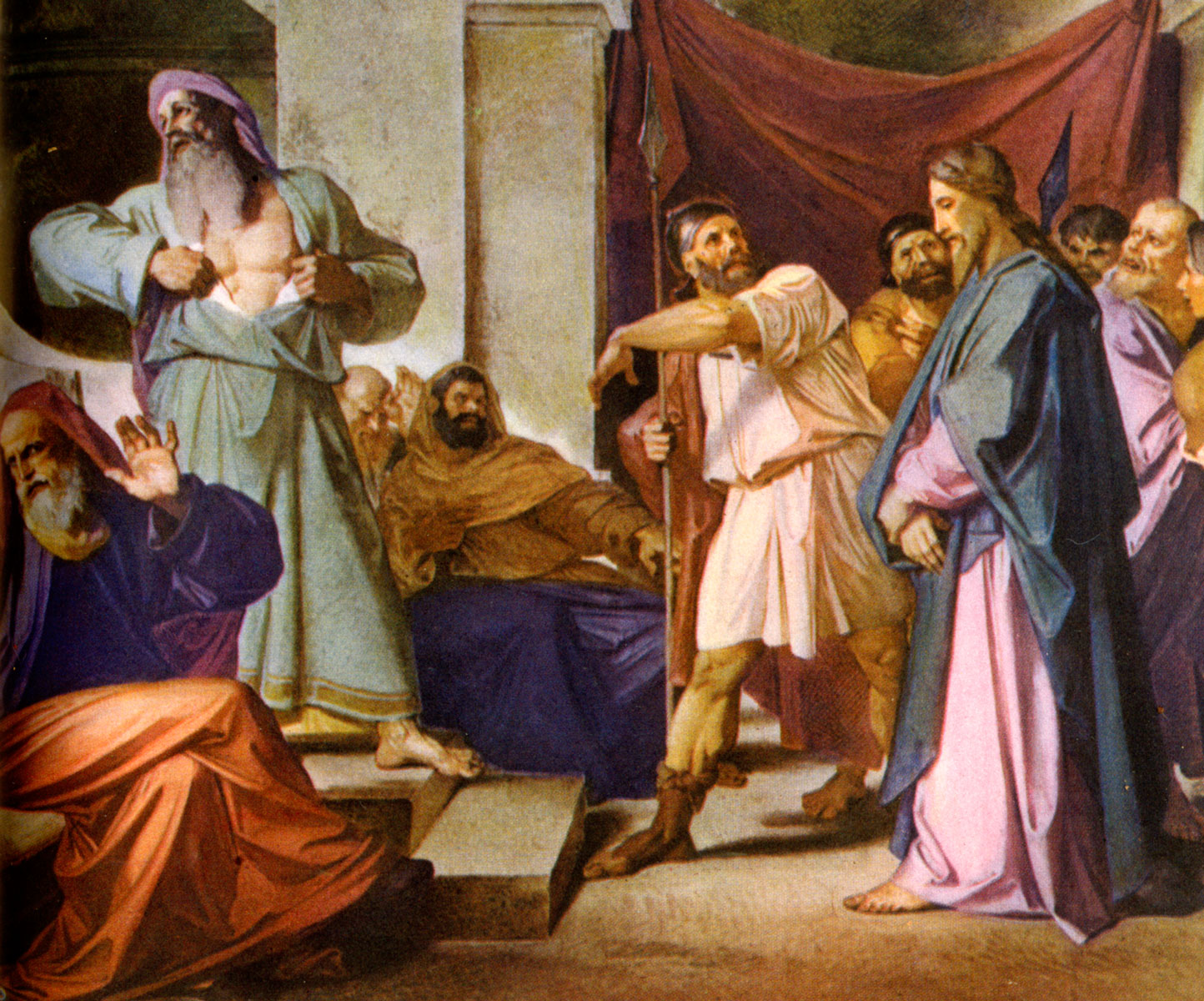

140. — How do we sin against faith?
We sin against faith when we:
1. Refuse to believe what God teaches us through His Church.
2. Willfully doubt any revealed truth.
3. Are ashamed or afraid to pass for a Christian, or formally deny the faith.
4. Neglect to learn Christian doctrine sufficiently.
5. Follow a way of life that is not in conformity with Christian beliefs.

141. — What do we call the sin of those who deny or who deliberately doubt a truth of faith?

142. — What do we call the sin of those who deny all the truths of faith?

143. — Is it a serious sin not to openly profess our faith in the true Church if we believe in it interiorly?

144. — Are we often obliged to make an open profession of our faith?

145. — How does faith diminish in the soul, and even reach the point of being lost?
Faith diminishes in the soul, and even reaches the point of being lost, by:
1. Neglect of religious duties.
2. Bad morals.
3. Reading literature or holding conversations which attack or question Catholic beliefs or which advocate neutrality.

146. — To accomplish the unity desired by Christ, must we not have an attitude of tolerance and openness to all religions?

147. — What is hope?

148. — Why do we hope for eternal life and the graces necessary to obtain it?

149. — What are the sins against hope?

150. — What is presumption?
Presumption is a rash expectation of salvation, by which:
1. We rely on the mercy of God as a license to commit sin and to delay our conversion.
2. We rely too much on our own strength to win heaven, without the grace of God, or without performing good works.

151. — What is despair?
Click on the dots to match the text to the audio.
Audio of the Lesson
Glossary
Theological: This qualifier given to the virtues of faith, hope and charity, comes from two Greek words, one meaning “God” and the other “speech”. The theological virtues are the virtues that have God as their object.
Faith: from the Latin “fides”, the word “faith” means “belief”. Faith is called divine or supernatural because it is a virtue that we cannot obtain by our own strength. And also because its object is supernatural, divine: God.
Hope: from the Latin “sperare”, which means “to hope”. God being the only object worthy of all our hope, and who alone can fill it perfectly, the virtue of hope makes us expect from Him supernatural goods and especially eternal happiness.
Charity: from the Latin “caritas”, which means “tenderness”. God is the only object worthy of all our love and He alone can fulfill every need of our heart and soul. Saint Augustine says, “You created us for You O God, and our hearts are restless until they rest all in You.”
Click here to download the complete Catechism Course.
This course is offered to you free of charge by Editions Magnificat.
You may download and print it for your personal use.
If you wish to make multiple copies, please request permission from:
apostles@magnificat.ca
THANK YOU!
© All rights reserved.
“I love them that love Me; and those that seek Me early shall find Me.”
Holy Scripture, Proverbs 8:17
“To fall in love with God is the greatest romance; to seek Him the greatest adventure; to find Him, the greatest human achievement.”
Saint Augustine












